Summary
Tortugas Harbor Lighthouse
This is an interactive virtual tour of Garden Key Light at Fort Jefferson, part of Dry Tortugas National Park in Florida. This tour is created from 360 panoramic photographs, taken by Heritage Documentation Programs staff while performing documentation fieldwork on site….
Source: National Park Service (.gov)

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the key functions of metabolism in living organisms?
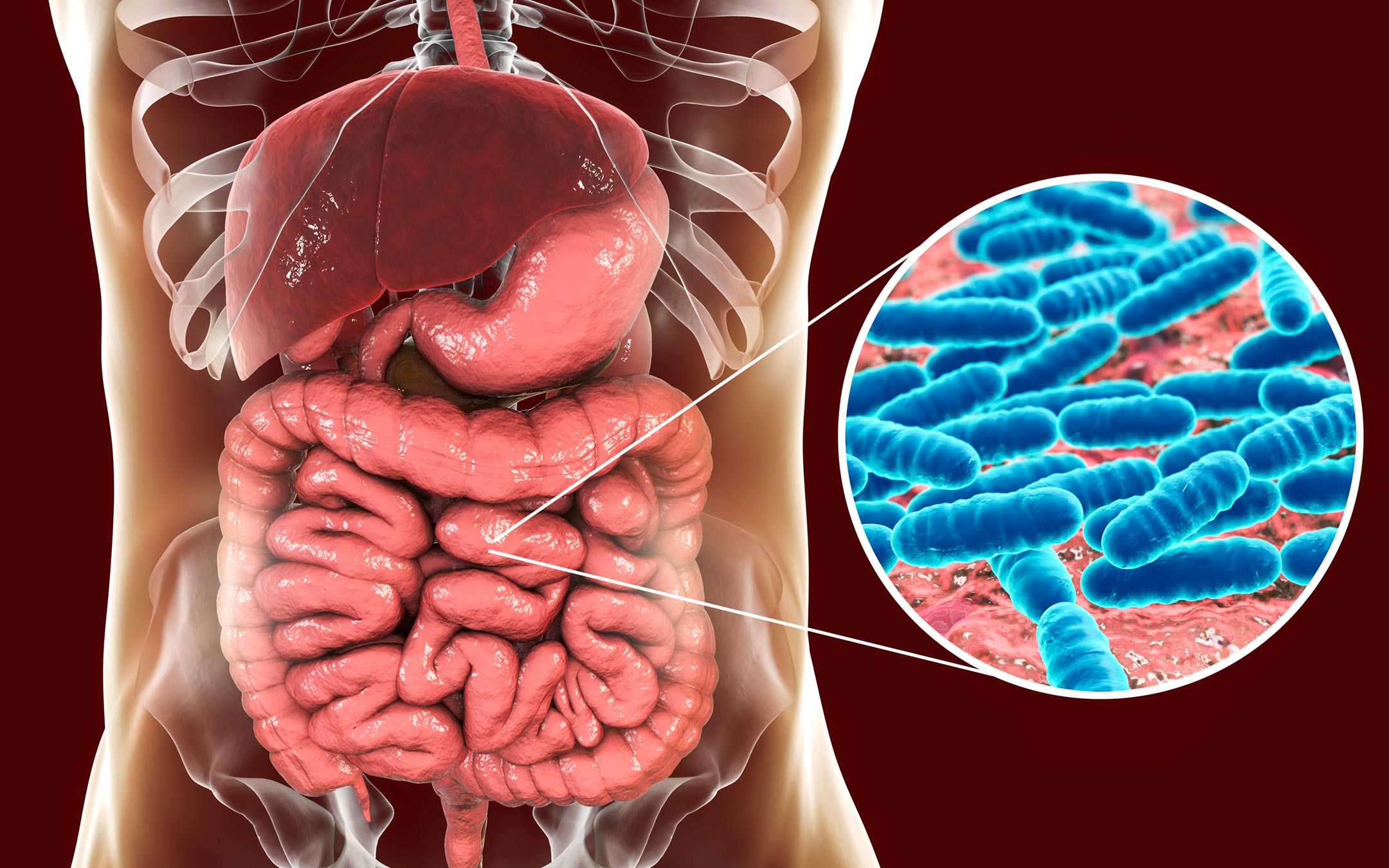
A1: Metabolism refers to the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions that occur within living organisms. Its three main functions include converting energy from food into a usable form for cellular processes, converting food to building blocks of macromolecules, and excreting metabolic wastes. These reactions are crucial for growth, reproduction, maintaining structures, and responding to environments. Metabolic pathways, facilitated by enzymes, allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy while coupling them to reactions that release energy.
Q2: How does obesity influence metabolic health and associated diseases?
A2: Obesity and its associated symptoms like high blood pressure and high blood sugar contribute to a condition known as metabolic syndrome. This syndrome increases the risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. NIH-funded research is focused on understanding how our bodies regulate calorie intake and burn, aiming to prevent and treat metabolic syndrome by examining the impact of behavior and environment on obesity.
Q3: What role does brown fat play in metabolic health?
A3: Brown fat significantly impacts metabolic health. In mice, activating brown fat reduces levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood, preventing atherosclerosis, which contributes to heart disease. In humans, more active brown fat is linked to lower rates of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and high blood pressure. Thus, increasing brown fat activity could protect against metabolic syndrome.
Q4: How can artificial intelligence improve health systems and public health performance?
A4: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can revolutionize healthcare delivery and patient engagement by integrating into digital health applications to improve health system performance. AI platforms can deliver adaptive interventions optimized through real-time monitoring and experimentation, significantly enhancing the impact of digital tools on health outcomes. This approach is particularly beneficial in resource-poor settings, where its impact on health outcomes could be more decisive.
Q5: What are the potential therapeutic avenues for managing scar development based on plasma metabolites?
A5: Recent research using Mendelian randomization analysis identified specific plasma metabolites associated with scar formation. Metabolites like (S)-α-amino-ω-caprolactam and N-acetylalanine are linked to increased scar risk, while alliin shows protective effects. These findings suggest that metabolic modulation could offer new therapeutic avenues for managing scar development.
Q6: What are the recommended biomarkers for assessing optimal metabolic health?
A6: Optimal metabolic health can be assessed using five biomarkers: fasting glucose levels under 100 mg/dL, triglyceride levels under 150 mg/dL, HDL cholesterol levels above 50 mg/dL for women and 40 mg/dL for men, a waist circumference of 35 inches max for women and 40 inches for men, and blood pressure at 120/80 mmHg. These markers help prevent chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Q7: How does the basal metabolic rate (BMR) influence energy consumption in the body?
A7: The basal metabolic rate (BMR) is a measure of the energy consumed by the body's chemical reactions at rest. It accounts for the largest portion of daily energy expenditure, ranging from 50% to 80%. BMR is influenced by factors such as age, gender, muscle-to-fat ratio, physical activity, and hormone function, impacting how much energy the body uses while maintaining normal functions like breathing and circulating blood.
References:
- Metabolism - Wikipedia
- Plasma metabolomics and scar pathogenesis: Insights from Mendelian randomization analysis
- Obesity and Metabolic Health - NIH Research Matters
- 5 Signs of Good Metabolic Health - Atlantic Health
- The Digital Transformation in Health: How AI Can Improve the Performance of Health Systems
- Better Health Channel - Metabolism

![Keep Fit Keto Gummies Reviews: Potential Benefits For Metabolic Health [SzoTN8Nc4um] - National Park Service (.gov) 1 defaultimg](https://consumers.app/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/defaultimg.png)