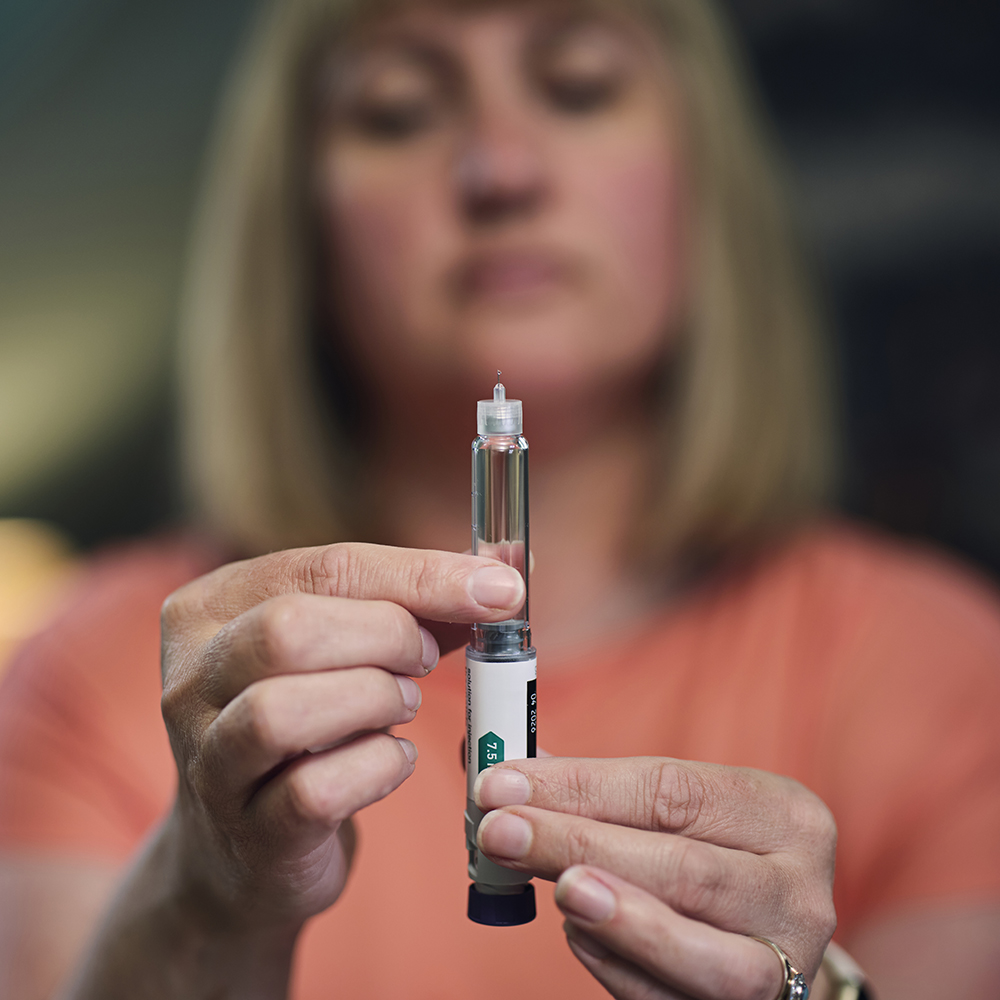Summary
A clinical trial involving patients from multiple health centers found that higher doses of semaglutide may help patients achieve greater weight loss without an increased risk of side effects. (Photo credit: Getty Images)
DALLAS Sept. 15, 2025 Tripling the standard dose of semaglutide, a popula…
Source: UT Southwestern Medical Center

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is semaglutide and how does it function in the body?
A1: Semaglutide is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and long-term weight management. It works as a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, which helps in lowering blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon release. It also slows gastric emptying and reduces appetite, contributing to weight loss.
Q2: What were the findings of the recent clinical trial on semaglutide regarding weight loss?
A2: The recent clinical trial found that higher doses of semaglutide significantly increased weight loss among patients without an increased risk of side effects. Patients experienced greater reductions in body weight compared to those on standard doses, indicating the drug's potential effectiveness for more substantial weight management.
Q3: What are the common side effects associated with semaglutide?
A3: Common side effects of semaglutide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation. These side effects are typically mild to moderate and decrease over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
Q4: How does semaglutide compare to other GLP-1 receptor agonists in terms of metabolic benefits?
A4: Semaglutide, like other GLP-1 receptor agonists, improves metabolic health by lowering glycated hemoglobin levels, improving lipid profiles, and reducing liver fat. It has shown significant benefits in weight reduction and cardiovascular health, making it a promising option for managing obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Q5: What are the latest advancements in incretin co-agonists for weight loss and metabolic health?
A5: Recent advancements in incretin co-agonists include the development of drugs like tirzepatide, which is a dual GIP/GLP-1RA. These drugs offer improved weight loss and metabolic health benefits with fewer gastrointestinal side effects. Other long-acting GLP-1RAs in development, such as Ecnoglutide and Efpeglenatide, show promising results in weight reduction and cardiovascular benefits.
Q6: How does the combination of cagrilintide and semaglutide enhance treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes?
A6: The combination of cagrilintide and semaglutide, marketed as CagriSema, enhances treatment by leveraging both amylin and GLP-1 receptor agonism. This dual approach not only improves glycemic control but also significantly aids in weight loss, making it a valuable option for managing obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Q7: What regulatory approvals does semaglutide have for its use in weight management?
A7: Semaglutide has been approved for medical use in the United States since 2017. It is used for weight management under the brand name Wegovy and is included in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Its effectiveness and safety in long-term weight management have been well-documented, leading to its widespread prescription.
References:
- Semaglutide - Wikipedia
- Efficacy and safety of incretin co-agonists: Transformative advances in cardiometabolic healthcare.
- Higher dose of semaglutide weight loss study 2025 - UT Southwestern Medical Center