Summary
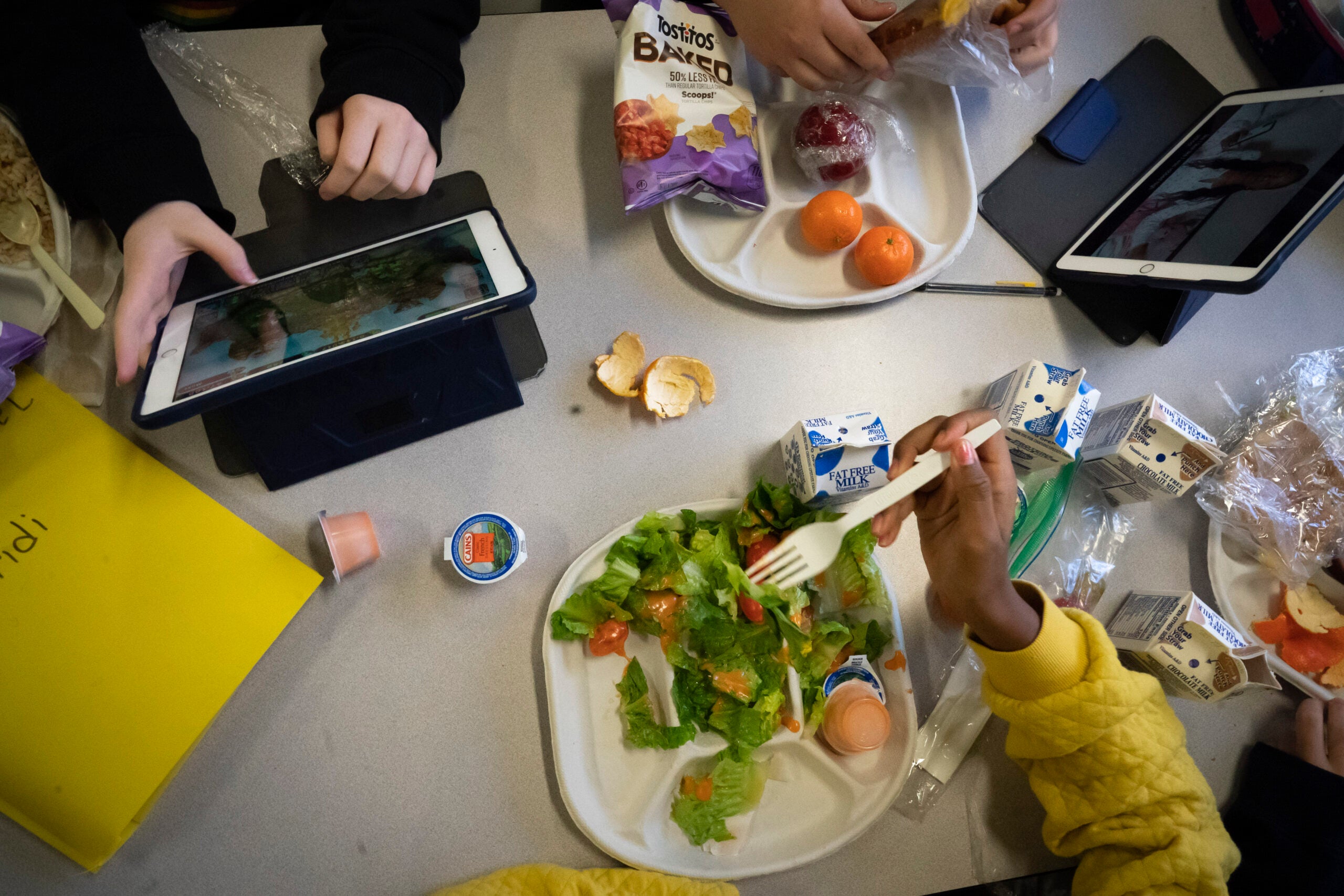
The state Assembly passed a bill Thursday that would ban schools from offering foods with certain ingredients in free or reduced-price meals.
The measure is in line with diet advice being pushed by U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., who has championed the so-called Ma…
Source: WPR

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the key provisions of the Wisconsin Assembly Bill 550 related to food additives?
A1: The Wisconsin Assembly Bill 550 mandates that manufacturers of packaged food products intended for human consumption must include prominent warning labels if the product contains any of the fifty-one ingredients listed in the bill. These include artificial colors, sweeteners, preservatives, and other additives. The labels must indicate that these ingredients are banned in Australia, Canada, the European Union, or the United Kingdom, with a specific warning statement for consumers.
Q2: How does the 'Make America Healthy Again' initiative influence recent legislative measures on food additives?
A2: The 'Make America Healthy Again' initiative, endorsed by U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy, Jr., has influenced legislative measures to ban certain food additives in schools. The Wisconsin Assembly passed a bill in line with this initiative to prohibit ingredients like brominated vegetable oil, potassium bromate, azodicarbonamide, propylparaben, and red dye 3 from being included in school meals. These measures aim to address concerns over processed foods and chemical additives contributing to childhood diseases.
Q3: What are some historical uses of food additives, and how have they evolved over time?
A3: Historically, food additives such as vinegar, salt, smoke, and sugar have been used for centuries to preserve food, extending the shelf life of products like bacon, sweets, and wines. With the rise of ultra-processed foods in the late 20th century, many natural and artificial additives were introduced to enhance taste, appearance, and preservation. Today, additives continue to play a significant role in the food industry, with strict regulations on their use and safety.
Q4: What are the health implications of synthetic food additives based on recent research?
A4: Recent research highlights that certain synthetic food additives may pose health risks, leading to legislative efforts to limit their use. Ingredients such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) have been scrutinized for potential links to health issues. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continues to review these additives to ensure they meet safety standards, while some jurisdictions have opted for stricter regulations.
Q5: How do E numbers relate to food additives in the European context?
A5: E numbers are codes assigned to food additives used within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). These codes help standardize the use of additives across member countries, ensuring that substances approved for use have undergone safety assessments by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The E number system facilitates transparency and consumer awareness regarding additives in food products.
Q6: What role do warning labels play in consumer awareness about food additives?
A6: Warning labels on food products serve to inform consumers about the presence of certain additives that may be banned or restricted in other countries. These labels aim to enhance consumer awareness and provide them with the information needed to make informed dietary choices. By highlighting the potential risks associated with specific additives, warning labels encourage manufacturers to consider safer alternatives.
Q7: What are some recent scientific advancements in the use of plant-based fat substitutes in food?
A7: Recent scientific advancements have focused on improving the freeze-thaw stability of plant-based fat substitutes, such as those derived from soybean protein isolate. Studies have shown that quick-freezing techniques, combined with specific thawing methods, can preserve the microstructure of these substitutes, maintaining their texture and stability. These innovations offer practical solutions for enhancing the quality of frozen plant-based foods.