Summary
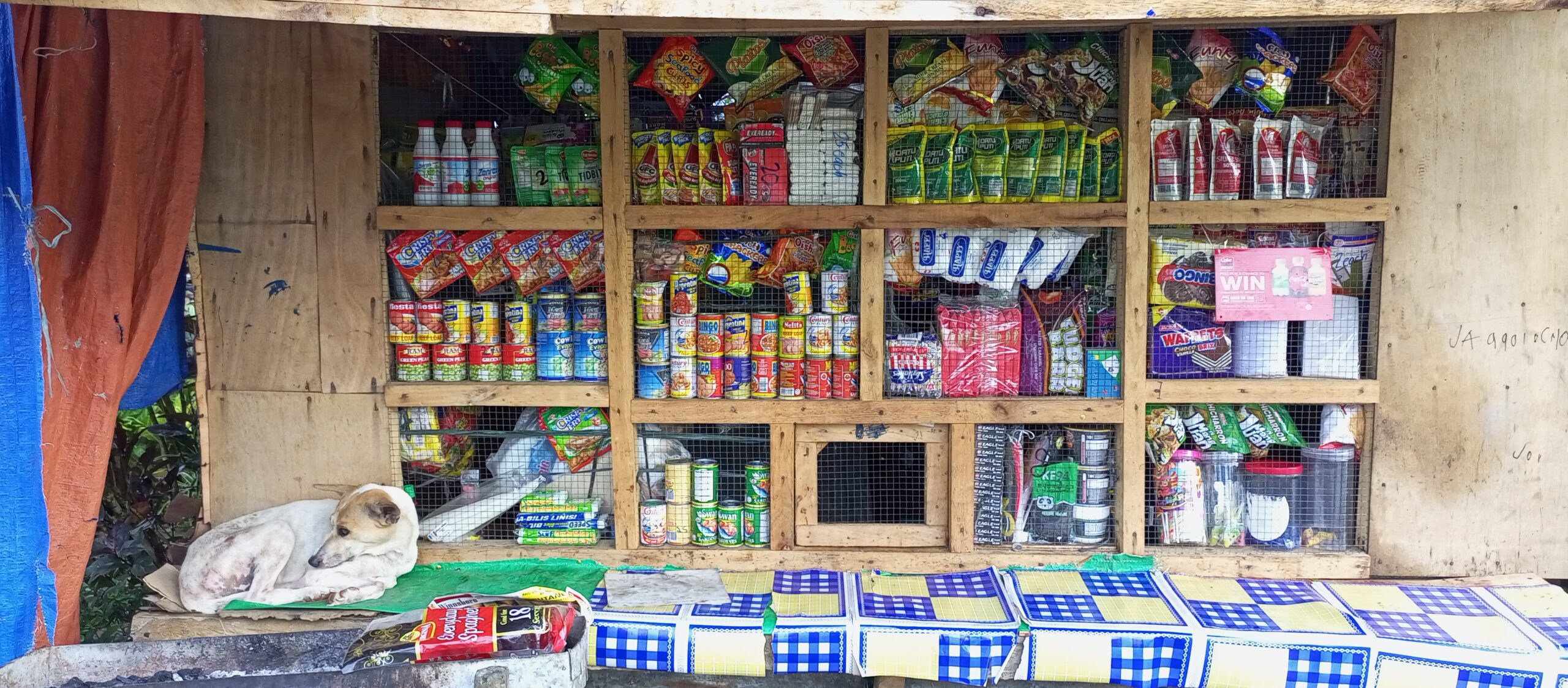
WHILE urban families spend more in supermarkets, rural households shell out more overall on weekly food expenses, according to the latest findings from the 2023 National Nutrition Survey. The report,
Source: BusinessMirror

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the key findings of the 2023 National Nutrition Survey regarding food expenditure in rural and urban areas?
A1: The 2023 National Nutrition Survey reveals that rural households spend more on food than urban ones. Specifically, rural areas allocate 47.04% of their monthly per capita consumption expenditure (MPCE) to food, while urban areas allocate 39.68%. This represents a slight increase from the previous year, indicating a possible trend reversal in food expenditure distribution.
Q2: How do nutritional supplements like chromium impact human nutrition according to recent studies?
A2: A narrative review on chromium supplementation suggests no beneficial effect on glycemia or serum lipids in individuals with or without type 2 diabetes. It challenges the essentiality of chromium as a trace mineral, indicating that its benefits might have been overstated in previous studies. Further randomized controlled trials are needed to draw conclusive results.
Q3: What does recent research say about the use of nutritional biomarkers in dietary assessments?
A3: Recent studies indicate that nutritional blood concentration biomarkers can mitigate subjective biases in self-reported dietary data. These biomarkers, including carotenoids and vitamins, show promise in accurately predicting diet-disease relationships, offering a more objective assessment of nutritional intake and its health impacts.
Q4: How has the trend in food expenditure changed between rural and urban areas according to the latest household consumption surveys?
A4: The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023-24 highlights a narrowing gap in food expenditure between rural and urban areas. Rural expenditure on food increased from 46.38% to 47.04%, while urban expenditure rose from 39.17% to 39.68%. This shift reflects changing consumption patterns and potentially declining inequality.
Q5: What are the implications of milk protein supplementation on health as per recent meta-analysis?
A5: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials finds that milk protein supplementation can significantly improve lipid profiles, lower blood pressure, reduce oxidative stress, and regulate liver enzyme levels. These outcomes suggest potential cardiovascular benefits, highlighting the importance of milk protein in dietary interventions.
Q6: How does food expenditure in rural areas compare to urban areas in the context of economic trends?
A6: Rural households spend a larger portion of their budget on food compared to urban households, with 47.04% versus 39.68% of MPCE respectively. This trend is influenced by economic factors such as income disparities and access to markets, which affect food affordability and consumption patterns.
References:
- Chromium Supplementation And The Essentiality Of Chromium To Human Nutrition: A Narrative Review
- Nutritional blood concentration biomarkers in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos: Measurement characteristics and power
- Impacts of Milk Protein Supplementation on Lipid Profile, Blood Pressure, Oxidative Stress, and Liver Enzymes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.