Summary
Vietnam, with more than 60% of its population living in rural areas, still relies heavily on traditional farming methods characterised by intensive resource use, low efficiency, and vulnerability to climate change. The circular economy offers new opportunities by using resources efficiently, maximis…
Source: Hortidaily

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the main challenges facing traditional farming methods in Vietnam, and how can a circular economy provide solutions?
A1: Traditional farming methods in Vietnam face challenges such as intensive resource use, low efficiency, and vulnerability to climate change. A circular economy can provide solutions by promoting efficient resource use, reducing waste, and enhancing sustainability. This approach encourages the recycling and reusing of materials, which can help mitigate the negative impacts of traditional farming on the environment.
Q2: How does the concept of circular economy apply to network management logic, and what benefits does it offer?
A2: The concept of circular economy applied to network management logic involves creating a circular workflow for software development, similar to product life cycles. By incorporating circular economy principles, the software life-cycle can reduce resource waste, including human effort and energy. The Socket Store, an online platform for modular network logic, exemplifies this approach, offering significant gains in resource efficiency.
Q3: What role do intelligent metasurfaces play in supporting circular economy principles?
A3: Intelligent metasurfaces can support circular economy principles by optimizing product designs and reducing resource waste. These metasurfaces can adjust their properties in response to software commands, enabling precise control over electromagnetic, acoustic, and mechanical properties. This adaptability allows for more sustainable product designs that align with circular economy goals by minimizing waste and improving resource efficiency.
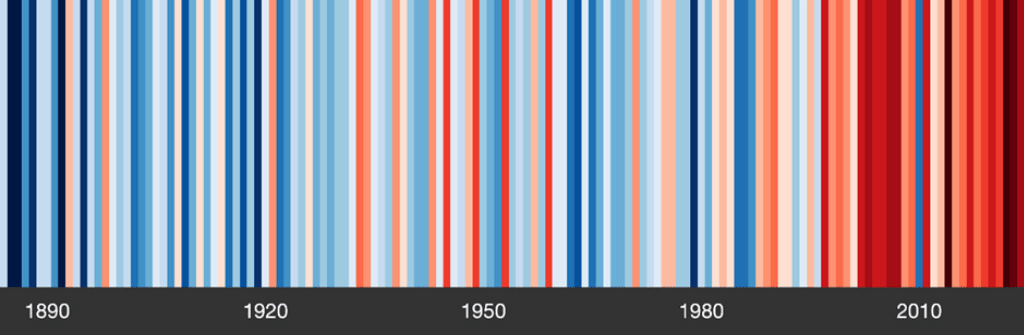
Q4: What are the potential environmental impacts of trade openness in Vietnam, particularly concerning CO2 emissions?
A4: Trade openness in Vietnam has been linked to increased CO2 emissions, with a growth rate of 7.26% annually. The Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis suggests an inverted U-shaped relationship between emissions and income per capita, indicating that emissions initially rise with economic growth but eventually decline. The Pollution Haven Hypothesis is also supported, showing that trade and energy use contribute to air pollution, though WTO membership has had positive environmental effects.
Q5: What sustainable practices can Vietnam adopt in agriculture to enhance the circular economy?
A5: Vietnam can enhance its circular economy in agriculture by adopting practices such as crop rotation, organic farming, and the use of renewable energy sources. These practices can improve resource efficiency, reduce waste, and decrease the carbon footprint of agricultural activities. Additionally, incorporating technology for better resource management and waste recycling can further support sustainable agricultural practices.
Q6: How does the implementation of a circular economy in agriculture contribute to a greener future for Vietnam?
A6: Implementing a circular economy in agriculture contributes to a greener future by promoting sustainable resource use, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact. This approach encourages recycling and reusing materials, leading to a decrease in pollution and a more resilient agricultural sector. By adopting circular economy practices, Vietnam can improve its environmental sustainability and reduce its vulnerability to climate change.
Q7: What are the broader socio-economic benefits of transitioning to a circular economy in Vietnam's agricultural sector?
A7: Transitioning to a circular economy in Vietnam's agricultural sector offers broad socio-economic benefits, including job creation, economic resilience, and improved food security. By reducing resource dependency and increasing efficiency, the circular economy can enhance productivity and competitiveness. This transition can also lead to healthier ecosystems, benefiting both local communities and the economy as a whole.
References:
- Towards a Circular Economy via Intelligent Metamaterials
- Organizing Network Management Logic with Circular Economy Principles
- The Effects of Trade Openness on CO2 Emission in Vietnam