Summary
The trillion-dollar merry-go-round: Inside AIs circular economy
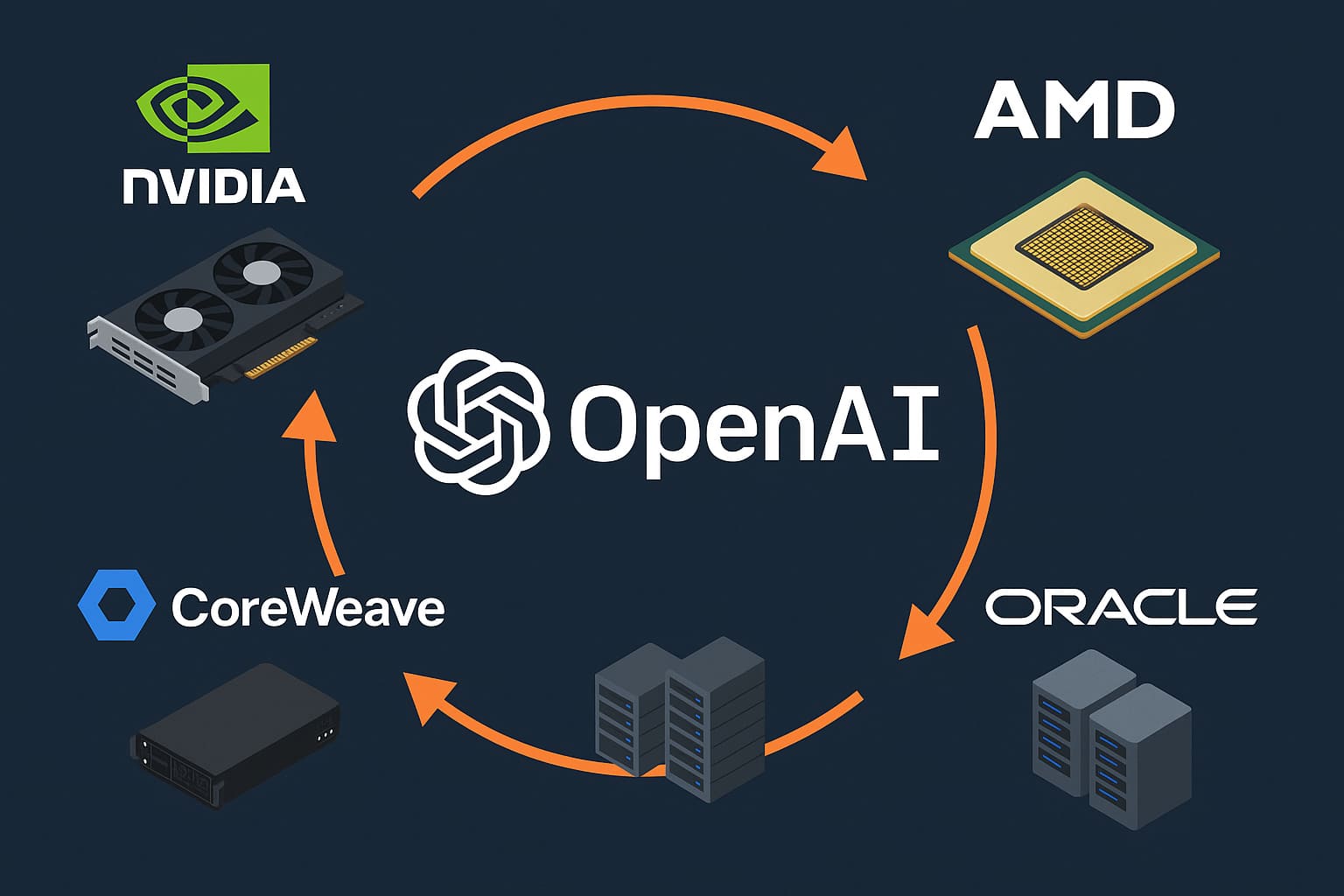
This week in AI, the story isnt about a breakthrough model or some transformational use case. Its about money…lots of money. From chipmakers to cloud giants, the AI economy is locked in a trillion-dollar loop of investments, GPU o…
Source: Moneycontrol

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the core principles of a circular economy, and how do they aim to tackle global challenges?
A1: The core principles of a circular economy include designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. These principles collectively aim to address global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution by ensuring that resources are reused and recycled for as long as possible, reducing the need for new raw materials, and minimizing carbon emissions.
Q2: How does AI investment influence firm productivity, particularly in the context of executive demographics?
A2: AI investment significantly influences firm productivity, with studies showing a 2.4% increase in total factor productivity. Executive demographics, such as age and technical background, play a crucial role, with younger executives (below 50 years) being 23% more likely to adopt AI technologies. This adoption impacts productivity through cost reduction, revenue enhancement, and innovation acceleration.
Q3: What role do business models play in transitioning to a circular economy?
A3: In a circular economy, business models such as product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, and product life extension are critical. These models help optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and create value for businesses and customers, facilitating the shift from linear to circular processes. They require a redesign of product concepts and service offerings towards long-life solutions.
Q4: How does the CircuGraphRAG framework enhance decision-making in the circular economy?
A4: The CircuGraphRAG framework improves decision-making by grounding large language model outputs in a domain-specific knowledge graph for the circular economy. This approach ensures accuracy and traceability by connecting industrial and waste entities with classification codes and emission data, enhancing regulatory and investment decisions through structured reasoning and efficient information retrieval.
Q5: What is the potential impact of circular economy strategies on global emissions?
A5: Implementing circular economy strategies in sectors like cement, aluminum, steel, plastics, and food can reduce global emissions by 9.3 billion metric tons of CO2 equivalent. This reduction is significant, equating to all current emissions from transportation, and highlights the potential for substantial environmental benefits through circular practices.
Q6: What challenges does openness in AI present, and how might it affect the circular economy?
A6: Openness in AI, including claims of open-source models and datasets, presents challenges related to power concentration among big tech leaders. However, it also offers opportunities for technological transfer and innovation in the circular economy by potentially reducing barriers for new entrants and fostering collaboration across the value chain.
Q7: How can circular economy practices influence long-term economic growth at the governmental level?
A7: Governments view the circular economy as a strategy for combating global warming and facilitating long-term growth. By promoting resource efficiency and sustainability, circular economy practices can open new market opportunities, reduce dependency on raw materials, and align with regulatory goals, thus supporting economic development and resilience.
References:
- Circular economy - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_economy
- AI Investment and Firm Productivity: How Executive Demographics Drive Technology Adoption and Performance in Japanese Enterprises - arXiv
- A Graph-Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework Enhances Decision-Making in the Circular Economy - arXiv
- Openness in AI and downstream governance: A global value chain approach - arXiv