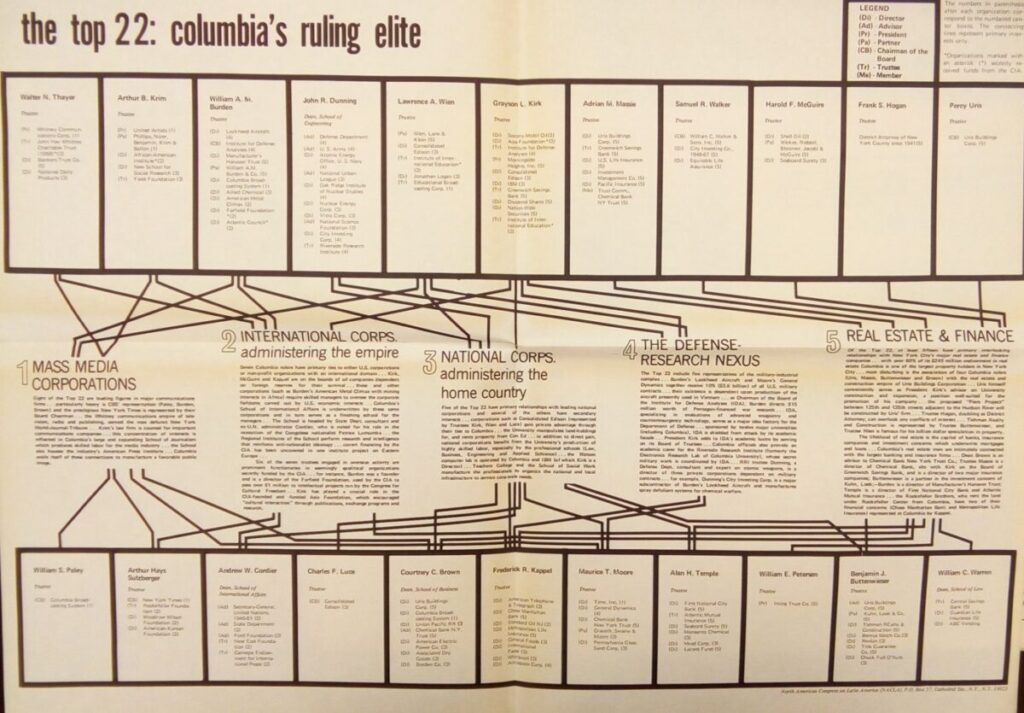
Summary
Today, its almost taken for granted that activist campaigns and organizing drives, including within the labor movement, have some form of a power
Source: zcomm.org

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is greenwashing, and why do companies engage in it?
A1: Greenwashing is a deceptive marketing practice where companies present themselves as environmentally friendly, often without substantiating their claims with real actions. Companies engage in greenwashing to appear legitimate and to project an environmentally responsible image to the public. The lack of a harmonized international definition makes it difficult for consumers and regulatory bodies to identify greenwashing effectively.
Q2: How does greenwashing impact consumer innovation, particularly in the retail sector?
A2: Greenwashing can stifle genuine consumer innovation by misleading consumers into believing that they are supporting sustainable practices when they are not. This can divert resources and attention away from truly innovative and sustainable practices in the retail sector, thereby hindering real progress towards sustainability.
Q3: Can you explain the findings of recent scholarly research on the influence of religiosity on corporate greenwashing behavior?
A3: Recent research has shown that firms located in areas with high religious adherence are less likely to engage in greenwashing. This is attributed to the influence of religious social norms, which promote risk aversion and discourage deceptive practices. The study conducted on US firms from 2005 to 2019 provides evidence that religious adherence can be a significant factor in reducing the incidence and magnitude of greenwashing.
Q4: What role do regulatory bodies play in combating greenwashing, and what challenges do they face?
A4: Regulatory bodies aim to protect consumers from misleading marketing practices by enforcing transparency and accountability. However, they face challenges such as the subjective nature of determining what constitutes greenwashing and the absence of a standardized global definition. This makes it difficult to regulate and penalize greenwashing effectively.
Q5: How does consumer perception influence greenwashing practices in companies?
A5: Consumer perception plays a crucial role in greenwashing practices. Companies exploit consumers' growing concern for the environment by crafting misleading messages that align with these values. This can lead to a false sense of ethical consumption, encouraging companies to invest more in greenwashing strategies rather than in genuine sustainable practices.
Q6: What are some examples of companies that have been accused of greenwashing, and what were the outcomes?
A6: Several companies have faced accusations of greenwashing, such as those in the fashion and automotive industries, which have exaggerated their environmental commitments. The outcomes often involve regulatory scrutiny, consumer backlash, and damage to brand reputation. Some companies have had to revise their marketing strategies and increase transparency to rebuild consumer trust.
Q7: What are some potential solutions to reduce greenwashing in consumer innovation?
A7: To reduce greenwashing, there needs to be increased consumer education on identifying genuine sustainability claims, along with stricter regulatory guidelines and enforcement. Companies should also be encouraged to adopt third-party certifications and transparent reporting practices to ensure accountability and authenticity in their sustainability efforts.
References:
- Greenwashing
- Does religiosity influence corporate greenwashing behavior?