AI News Q&A (Free Content)
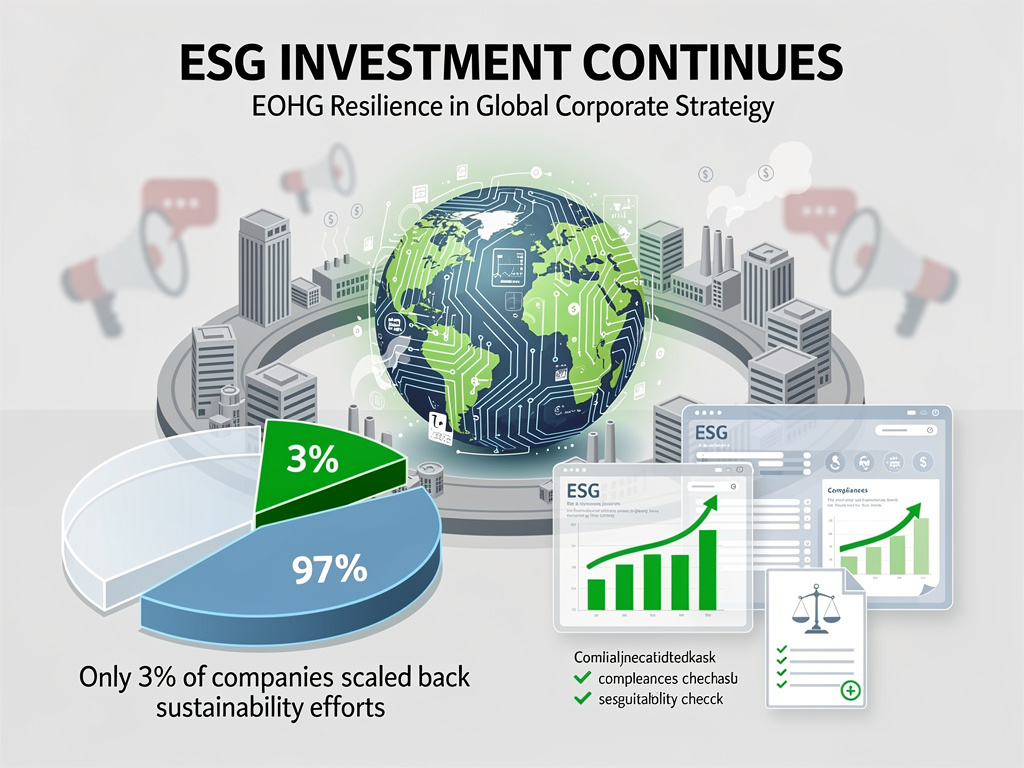
Q1: What is the '3% Paradox' and why are major companies focusing more on sustainability despite the anti-ESG backlash?
A1: The '3% Paradox' refers to the observation that although a small percentage of companies are explicitly committed to sustainability, nearly all major companies are increasing their sustainability efforts despite facing backlash against Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. This is driven by consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices, regulatory pressures, and the long-term financial benefits of sustainable operations.
Q2: How has the recent surge in inflation affected global sustainability initiatives among major companies?
A2: The inflation surge from 2021 to 2023 created challenges for companies, including higher operational costs. Despite these economic pressures, many companies have continued to prioritize sustainability to future-proof their operations against supply chain disruptions and regulatory changes. The focus on sustainability is seen as a strategic decision to mitigate long-term risks and capitalize on evolving market demands.
Q3: What are the key findings of the study 'Measuring Sustainability Intention of ESG Fund Disclosure using Few-Shot Learning'?
A3: The study proposes a method to evaluate the sustainability claims of ESG funds by analyzing the language used in their prospectuses. It introduces a scoring system for evaluating the clarity and specificity of sustainability intentions, using few-shot learning techniques. The research highlights the need for more transparent sustainability claims and provides a tool for regulators and investors to assess ESG funds more effectively.
Q4: How does the ESG-FTSE corpus contribute to understanding ESG relevance in news articles?
A4: The ESG-FTSE corpus is a collection of news articles annotated with ESG relevance labels. It helps in identifying articles that are relevant to ESG topics, enabling better assessment of ESG scores. The corpus supports both supervised and unsupervised learning, facilitating accurate predictions of ESG relevance and contributing to more informed ESG investments.
Q5: What is the impact of the anti-ESG movement on corporate strategies towards sustainability?
A5: The anti-ESG movement, which critiques the focus on ESG criteria as potentially detrimental to financial performance, has led to increased scrutiny of ESG initiatives. However, many corporations view sustainability as integral to their long-term strategy, aiming to balance ESG concerns with financial performance. The backlash has prompted some companies to improve transparency and communication about the benefits of their sustainability efforts.
Q6: What role do regulatory bodies play in enforcing sustainability in ESG products?
A6: Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on ensuring that ESG products meet genuine sustainability criteria. They aim to create standards and guidelines that prevent greenwashing and ensure that products marketed as sustainable adhere to rigorous environmental and social standards. This regulatory oversight is crucial for maintaining investor trust and promoting responsible investment practices.
Q7: How are new technologies influencing the measurement and implementation of sustainability in companies?
A7: Technological advancements, such as data analytics and machine learning, are enhancing the measurement and implementation of sustainability. These technologies allow companies to track their environmental impact more accurately, optimize resource use, and improve the transparency of their sustainability claims. Innovations like the ESG-FTSE corpus and few-shot learning techniques are examples of how technology can support more informed sustainability strategies.
References:
- Page: 2021–2023 inflation surge
- Measuring Sustainability Intention of ESG Fund Disclosure using Few-Shot Learning
- ESG-FTSE: A corpus of news articles with ESG relevance labels and use cases