Summary
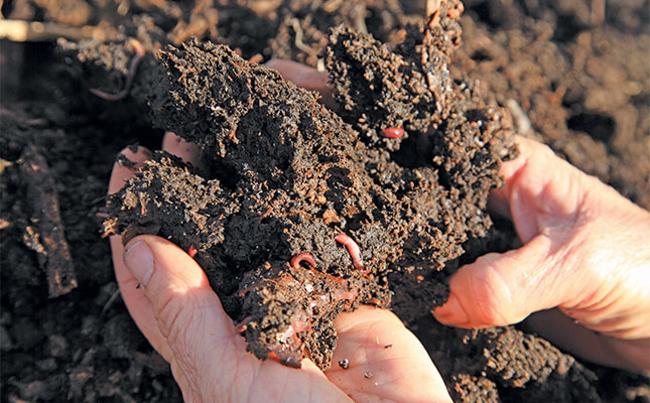
Whether youre growing winter crops or raising livestock, healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture. Sheila Storey, co-founder and consultant at the Soil Health Support Centre, spoke to Glenneis Kriel about how farmers can evaluate and improve their soil health.
Source: Farmer's Weekly

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the key factors that contribute to maintaining soil health in agriculture?
A1: Maintaining soil health in agriculture involves a combination of practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and organic amendments. These practices enhance soil organic matter, improve nutrient cycling, and maintain a healthy soil microbiome. Soil testing is crucial to understand soil conditions and adjust management practices accordingly. Inorganic fertilizers, if used judiciously, can also contribute positively by supporting plant growth and increasing carbon inputs to the soil.
Q2: How does sustainable agriculture address the environmental challenges posed by traditional farming methods?
A2: Sustainable agriculture mitigates environmental challenges by employing farming practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, prevent soil degradation, and conserve water. Techniques such as agroforestry, permaculture, and using bio-inoculants help in maintaining ecosystem balance. These practices aim to produce food without compromising future generations' ability to meet their needs, thereby contributing to climate change mitigation and resource conservation.
Q3: What role do microbial inoculants play in enhancing soil health for sustainable agriculture?
A3: Microbial inoculants, such as nitrogen-fixers and phosphorus solubilizers, play a significant role in enhancing soil health by improving nutrient availability, suppressing pathogens, and increasing plant resilience to stresses such as drought and salinity. They support sustainable agriculture by reducing dependency on chemical fertilizers, thereby maintaining soil fertility and biodiversity.
Q4: What innovative technologies are being used to improve soil health in agricultural practices?
A4: Innovative technologies such as AI-driven Soil Organic Carbon Copilots and sensor-based monitoring systems are being used to improve soil health. These technologies enable real-time data collection on soil conditions, helping farmers make informed decisions on soil management. By integrating machine learning algorithms, farmers can optimize practices such as irrigation and fertilization to enhance productivity while maintaining soil health.
Q5: How can farmers evaluate soil health in their fields effectively?
A5: Farmers can evaluate soil health through a combination of field assessments and laboratory tests. Field assessments include observing soil color, texture, and smell, as well as checking for earthworms and root nodulation. Laboratory tests can measure active carbon, electrical conductivity, pH, and nutrient levels. Regular monitoring allows farmers to make timely interventions to maintain or improve soil health.
Q6: What are the benefits of using regenerative agricultural practices for soil health?
A6: Regenerative agricultural practices, such as composting and minimizing tillage, offer numerous benefits for soil health. These practices increase soil organic matter, enhance microbial diversity, and improve soil structure. By building soil carbon stocks, they also contribute to carbon sequestration, which helps mitigate climate change. Overall, regenerative practices create resilient agricultural systems that are more productive and sustainable.
Q7: What challenges do farmers face when implementing sustainable soil management practices?
A7: Farmers face challenges such as the initial cost of transitioning to sustainable practices, lack of technical knowledge, and uncertain financial returns. There are also regional variations in soil types and climates that require tailored approaches. Additionally, access to resources like quality compost or suitable cover crop seeds can be limited. Overcoming these challenges requires support through policy incentives, education, and access to technology.
References:
- Page: Soil health
- Page: Sustainable agriculture
- Enabling Adoption of Regenerative Agriculture through Soil Carbon Copilots
- Transforming Agriculture: Exploring Diverse Practices and Technological Innovations
- EcoWeedNet: A Lightweight and Automated Weed Detection Method for Sustainable Next-Generation Agricultural Consumer Electronics
- Soil Health Support Centre Sheila Storey
- How to evaluate and improve soil health in agriculture
- Microbial inoculants - fostering sustainability in groundnut production