Summary
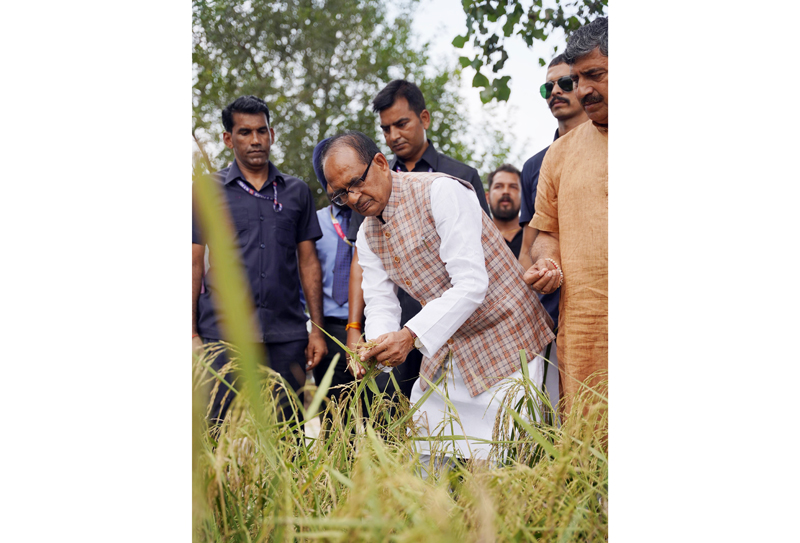
Chouhan announces slew of measures for flood-hit people Centre, JK Govts will take steps to restore livelihoods hit by rains Sanjeev Pargal JAMMU, Sept 19: Unio…
Source: dailyexcelsior.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) and how does it aim to support flood-affected people in India?
A1: The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) is a government initiative in India designed to provide affordable housing to low and moderate-income residents. It has two components: PMAY-Urban (PMAY-U) for the urban poor and PMAY-Rural (PMAY-R) for the rural poor. The scheme converges with other initiatives to ensure homes have essential services such as toilets, electricity, and water. In the context of flood-affected areas, PMAY can play a critical role in rebuilding and providing safe housing to those displaced by floods, aiding in the restoration of livelihoods.
Q2: How does weather index insurance benefit smallholder farmers in India, particularly in the face of floods?
A2: Weather index insurance offers financial protection to smallholder farmers in India by compensating them for losses resulting from adverse weather conditions, such as floods. A study indicates that seasonal weather variations significantly impact crop yield variance. This insurance model helps farmers manage risk and ensures financial stability despite unpredictable weather, which is crucial for maintaining agricultural productivity and livelihoods.
Q3: What recent scholarly advancements have been made in developing a flood severity index in India?
A3: A recent development in India is the creation of the India Flood Inventory with Impacts (IFI-Impacts) database, which includes a District Flood Severity Index (DFSI). This index measures the severity of floods based on historical data, including fatalities and damages, across Indian districts. The DFSI helps in planning and implementing flood mitigation and relief measures, making it an essential tool for disaster preparedness and management.
Q4: What role do Self Help Groups (SHGs) play in flood relief efforts in India?
A4: Self Help Groups (SHGs) in India are vital in flood relief efforts as they facilitate community-based approaches to recovery and resilience. They often receive government and non-governmental funding to support local initiatives, such as rebuilding infrastructures, providing microloans, and ensuring food security. SHGs empower communities to manage resources effectively and collectively respond to disasters like floods.
Q5: What are the challenges in implementing crop insurance schemes effectively in flood-prone regions of India?
A5: Implementing crop insurance schemes in flood-prone regions of India faces several challenges, including low uptake rates due to a lack of awareness and trust among farmers. Additionally, accurately assessing and pricing risk is complex due to the variability of weather patterns and insufficient historical data. These challenges necessitate improved outreach, better-designed insurance products, and robust data collection methods to enhance the efficacy of such schemes.
Q6: How does the PMAY scheme integrate with other welfare programs to support flood-affected populations?
A6: The PMAY scheme integrates with various welfare programs to provide comprehensive support to flood-affected populations. For instance, it aligns with the Saubhagya Scheme for electricity, Ujjwala Yojana for clean cooking fuel, and efforts to ensure access to clean water and banking services. This integrated approach ensures that beneficiaries receive a holistic package of services essential for rebuilding their lives post-disaster.
Q7: What innovative measures are being developed to reduce the impact of floods on urban areas in India?
A7: Innovative measures to reduce the impact of floods on urban areas in India include the development of models like FloodGenome, which uses machine learning to assess flood risk predisposition. This model evaluates various factors such as hydrological, topographic, and built-environment features to shape flood risk profiles in urban settings. These insights enable the design of better urban flood management strategies and risk reduction plans.
References:
- Risk, Agricultural Production, and Weather Index Insurance in Village India
- A District-level Flood Severity Index for Flood Management in India
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
- FloodGenome: Interpretable Machine Learning for Decoding Features Shaping Property Flood Risk Predisposition in Cities