Summary
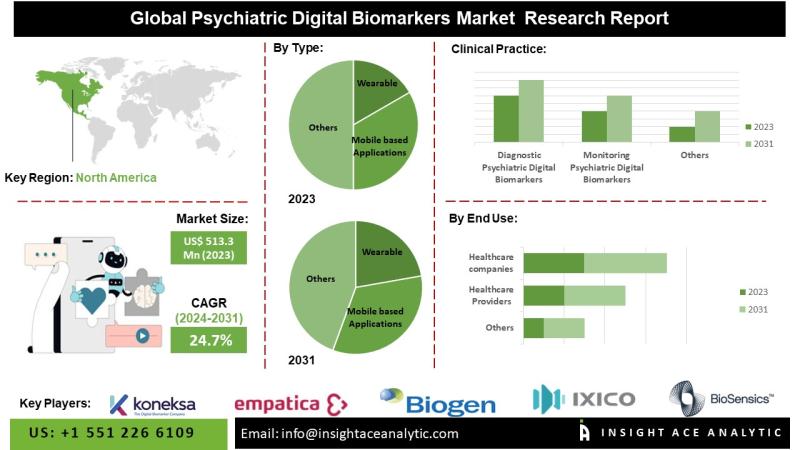
InsightAce Analytic Pvt. Ltd. announces the release of a market assessment report on the Psychiatric Digital Biomarkers Market-, By Type (Wearable, Mobile based Applications, Sensors) Clinical Practice (Diagnostic Psychiatric Digital Biomarkers, Monitoring Psychiatric Digital Biomarkers, Predictive and Prognostic Psychiatric Digital
Source: Openpr.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are psychiatric digital biomarkers and how are they transforming the field of mental health diagnostics?
A1: Psychiatric digital biomarkers are objective, quantifiable physiological and behavioral data that are collected and measured by digital devices like wearables, mobile applications, and sensors. These biomarkers are transforming mental health diagnostics by enabling continuous monitoring and real-time data collection outside of clinical settings, which can lead to earlier diagnosis and more personalized treatment plans. This approach allows for the observation of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral patterns in natural environments, potentially improving the accuracy of mental health assessments and interventions.
Q2: How does the JTrack platform utilize digital biomarkers for remote monitoring of psychiatric conditions?
A2: The JTrack platform employs digital biomarkers to facilitate remote monitoring in neurological and psychiatric diseases through an Android-based smartphone application and a web-based dashboard. It collects anonymized data from motion sensors, social and physical activities, and geolocation information. This platform is designed to comply with privacy and data protection regulations, offering a scalable and reproducible data management solution. JTrack enhances the ability to gather insights into daily life behaviors, helping clinicians to monitor patients' conditions remotely and adjust treatments as needed.
Q3: What role do audiovisual digital biomarkers play in psychiatric research, according to recent studies?
A3: Audiovisual digital biomarkers are increasingly being tested in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorder research. These biomarkers allow for the extraction of patient behavior changes through open-source software, promoting accessibility and integration in clinical research. The OpenDBM Analytics Tool, for example, supports interactive visual analysis of behavioral data, helping non-technical experts explore patterns and facilitate the adoption of digital biomarkers in both basic and applied research.
Q4: What advancements have been made in using resting-state functional connectivity MRI as a digital biomarker for psychiatric disorders?
A4: Resting-state functional connectivity MRI (rs-fcMRI) is being developed as a digital biomarker to bridge the gap between psychiatric symptoms and their neural underpinnings. This approach aims to redefine psychiatric disorders based on neural circuitry rather than symptoms alone. rs-fcMRI biomarkers are used for data-driven diagnosis and to identify therapeutic targets, potentially leading to more personalized treatment strategies and better prediction of therapy efficacy.
Q5: What are the potential economic impacts of the growth in the psychiatric digital biomarkers market by 2034?
A5: The psychiatric digital biomarkers market is expected to grow significantly by 2034, driven by advancements in wearable technology, mobile applications, and sensors. This growth could lead to reduced healthcare costs by enabling early detection and personalized treatment plans, decreasing the need for in-clinic visits, and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the integration of digital biomarkers into healthcare systems may foster innovation and create job opportunities in the tech and healthcare sectors.
Q6: How do digital biomarkers address the challenges of traditional psychiatric assessments?
A6: Digital biomarkers offer solutions to traditional psychiatric assessment challenges by providing continuous, objective data collection in naturalistic settings. Unlike episodic and often subjective in-clinic assessments, digital biomarkers can capture real-time changes in behavior and physiology, leading to more accurate and dynamic understanding of mental health conditions. This continuous data flow helps clinicians to detect mood shifts, predict relapses, and tailor interventions more effectively.
Q7: What are the privacy and ethical considerations associated with using digital biomarkers in mental health monitoring?
A7: The use of digital biomarkers in mental health monitoring raises several privacy and ethical concerns. These include ensuring data security, obtaining informed consent, and maintaining patient confidentiality. Platforms like JTrack are designed to comply with privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), but ongoing vigilance is needed to protect sensitive health data. Ethical considerations also involve the potential for misuse of data and ensuring equitable access to digital health technologies.
References:
- Psychiatry - Wikipedia
- JTrack: A Digital Biomarker Platform for Remote Monitoring in Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases
- Opening Access to Visual Exploration of Audiovisual Digital Biomarkers: an OpenDBM Analytics Tool
- Resting-state functional connectivity-based biomarkers and functional MRI-based neurofeedback for psychiatric disorders