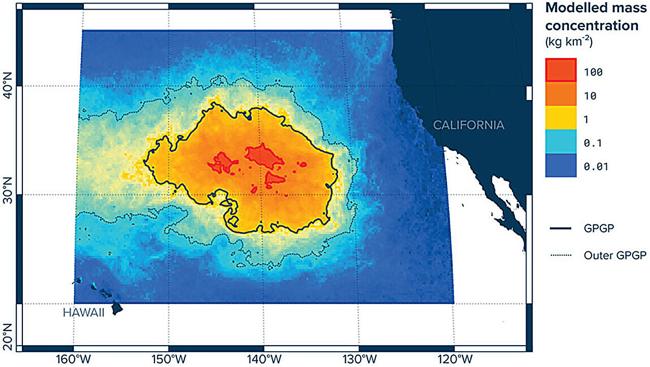
Summary
Professor Richard Thompson led the first study using the term microplastics to describe microscopic fragments of plastic polluting oceans
Source: Plymouth Live on MSN.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: Who is Professor Richard Thompson and why was he named among TIME's 100 most influential people in 2025?
A1: Professor Richard Thompson is a marine biologist known for his pioneering research on marine litter and the introduction of the term 'microplastics' in 2004. His work has significantly contributed to understanding the impact of microplastics on marine environments and human health. TIME magazine recognized his influence in 2025 due to his groundbreaking work in the field, highlighting his role in raising global awareness about plastic pollution.
Q2: What are microplastics, and how do they contribute to environmental pollution?
A2: Microplastics are tiny plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size that originate from the breakdown of larger plastic debris or are manufactured as small particles for consumer products. They enter ecosystems through various sources, including textiles, cosmetics, and industrial processes, and cause pollution by persisting in aquatic, terrestrial, and aerial environments, impacting wildlife and potentially human health.
Q3: What are the health implications of microplastics, particularly concerning human health?
A3: Microplastics pose significant health risks as they can infiltrate human biological systems. Recent studies have linked microplastic exposure to adverse birth outcomes, such as low birth weight, and gastrointestinal health issues, including gut microbiota disruption and inflammation. This highlights the urgent need for policies to mitigate their presence in the environment.
Q4: How do microplastics impact marine life and ecosystems?
A4: Microplastics impact marine life by being ingested by aquatic organisms, which can lead to physical harm, chemical exposure, and biomagnification up the food chain. This pollution disrupts marine ecosystems, affecting biodiversity and ecological balance.
Q5: What innovative methods are being developed to identify and manage microplastic pollution?
A5: Innovative methods like AI-driven image segmentation and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are being developed to improve the identification of microplastics in water samples. These technologies enhance detection accuracy and accessibility, enabling better management of microplastic pollution.
Q6: What recent research suggests about the potential pathways of microplastics affecting human health?
A6: Recent research suggests that microplastics can become airborne through aerosolization, particularly from seawater evaporation, posing inhalation risks. This pathway is significant as it increases the likelihood of microplastic exposure, emphasizing the importance of addressing this issue as ocean temperatures rise.
Q7: What are the policy recommendations to address microplastic pollution and its effects?
A7: Policy recommendations include reducing the production and usage of disposable plastics and implementing stricter regulations on plastic waste management. These measures aim to decrease microplastic contamination, promote environmental sustainability, and safeguard human health.
References:
- Microplastics
- Richard Thompson (marine biologist)
- Marine Microplastics and Infant Health
- Microplastic Identification Using AI-Driven Image Segmentation and GAN-Generated Ecological Context
- Impacts of microplastics on gut health: Current status and future directions.
- Assessing the efficacy of electrocoagulation process for polypropylene microplastics removal from wastewater: Optimization through TOPSIS approach.