Summary
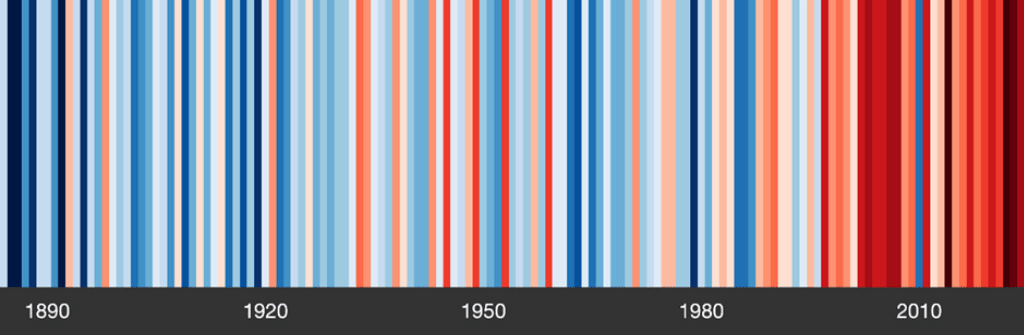
The New Mexico Environment Department on Friday published a Climate Action Plan that contains more than three dozen steps to meet Gov. Michelle Lujan Grishams goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
NMED officials collaborated with their counterparts at the Energy, Minerals and Natural Res…
Source: Source New Mexico

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the main goals of the New Mexico Environment Department's Climate Action Plan?
A1: The primary goal of the New Mexico Environment Department's Climate Action Plan is to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. This plan outlines over three dozen steps aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions in line with Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham's environmental objectives.
Q2: How does the concept of a biodiversity action plan relate to climate action efforts?
A2: A biodiversity action plan (BAP) is designed to protect and restore threatened species and habitats. It complements climate action efforts by enhancing ecosystem resilience, which is crucial for mitigating climate change impacts, such as desertification and habitat loss.
Q3: What are some of the challenges in managing Mediterranean ecosystems under changing climate conditions?
A3: Mediterranean ecosystems face challenges from invasive species, increased fire risk, and toxin release due to climate change. Human activities and climate warming have altered these ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to destructive wildfires and ecological disruption.
Q4: How does climate change impact precipitation extremes globally?
A4: Climate change intensifies precipitation extremes, making heavy rainfall events more intense and frequent. However, the sensitivity of these extremes can vary, especially in regions with significant convective activity, such as the tropics. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for climate modeling and mitigation strategies.
Q5: In what ways has anthropogenic climate change affected the East Asian summer monsoon?
A5: Anthropogenic climate change has reduced total monsoon rainfall over Eastern China while increasing the frequency of dry days. Extreme heavy rainfall events have become shorter but more intense, highlighting the complex influence of human activities on regional climate patterns.
Q6: What are some strategies to minimize the future impacts of climate change?
A6: Strategies to minimize climate change impacts include phasing out fossil fuels, conserving energy, and transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. Additionally, implementing flood control measures and developing drought-resistant crops can help societies adapt to climate risks.
Q7: Why is it essential to consider both mitigation and adaptation in climate action plans?
A7: Mitigation and adaptation are both essential in climate action plans because mitigation addresses the root causes by reducing emissions, while adaptation focuses on managing the impacts. Together, they offer a comprehensive approach to lessening climate change risks and enhancing resilience.
References:
- Biodiversity action plan
- Climate change
- Invasive species, extreme fire risk, and toxin release under a changing climate
- Climate Change Institute, School of Earth, Climate Sciences, University of Maine
- Precipitation extremes under climate change
- Paul A. O'Gorman
- Impact of anthropogenic climate change on the East Asian summer monsoon
- Claire Burke, Peter Stott