Summary
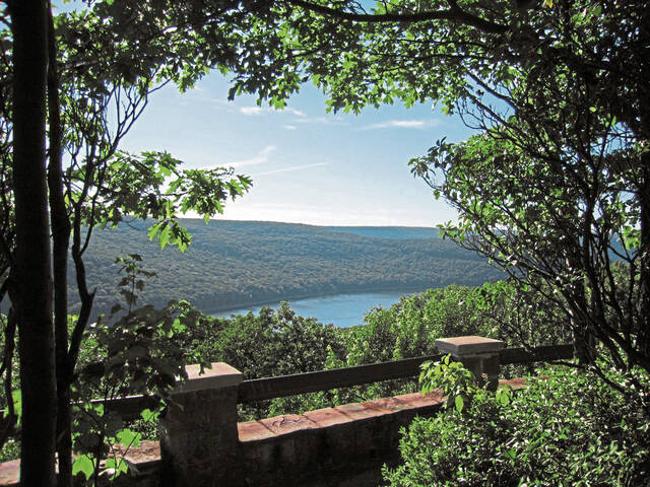
Swaths of Allegheny National Forest in northwestern Pennsylvania could be on the chopping block as the federal government moves to increase logging in national forests across the country, a move environmental advocates say could leave lasting harm.
Source: TribLive

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the current logging situation in the Allegheny National Forest, and what prompted the emergency declaration?
A1: The Allegheny National Forest, covering 513,175 acres in northwestern Pennsylvania, is under an emergency declaration to accelerate logging. This move is part of a broader federal initiative to increase logging in national forests across the United States. Environmental advocates express concern over potential lasting harm, as the forest is a critical ecosystem with diverse flora and fauna, contributing to the state's oil production.
Q2: How does the Allegheny National Forest contribute to Pennsylvania's ecological and economic landscape?
A2: The Allegheny National Forest is a vital ecological region that supports biodiversity and serves as a habitat for various species. Economically, it is located in Pennsylvania's oil and gas region and contributes to the state's crude oil production. The forest's proximity to the first commercial oil well in the U.S. underscores its historical and economic significance.
Q3: What are the potential environmental impacts of increased logging in national forests?
A3: Increased logging in national forests can disrupt ecosystems, reduce biodiversity, and degrade habitats. It may also affect carbon sinks and contribute to climate change. Scholarly research indicates that such activities should be managed carefully to balance economic needs with environmental sustainability, as highlighted in studies on forest management and systemic complexity.
Q4: What are some of the complexities involved in managing forest ecosystems sustainably?
A4: Managing forest ecosystems sustainably involves understanding their complexity, which includes diverse landscapes, microclimates, and species interactions. Research suggests incorporating unpredictability and control challenges into environmental impact assessments and management programs, ensuring that conservation efforts maintain the forest's ecological integrity.
Q5: How does the biodiversity of the Appalachian–Blue Ridge forests compare to that of the Allegheny National Forest?
A5: The Appalachian–Blue Ridge forests, known for their rich biodiversity, are among the world's richest temperate deciduous forests. The Allegheny National Forest shares similar ecological traits, providing diverse habitats and supporting numerous species. Both regions' biodiversity is attributed to geological stability and varied microhabitats.
Q6: What are the implications of logging on the carbon footprint of forest ecosystems?
A6: Logging can significantly impact the carbon footprint of forest ecosystems by reducing their ability to function as carbon sinks. Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, and increased logging can disrupt this balance, potentially contributing to increased atmospheric carbon levels and affecting climate change mitigation efforts.
Q7: What strategies are recommended for balancing economic and environmental needs in forest management?
A7: Balancing economic and environmental needs in forest management requires adopting sustainable practices that consider long-term ecological health. Strategies include integrating spatial data for better forest type predictions, understanding systemic complexity, and using environmental indicators to guide conservation efforts. These approaches help maintain biodiversity while supporting economic activities like logging.
References:
- Allegheny National Forest - Wikipedia
- More than trees, do we need a complex perspective for sustainable forest management?