Summary
Intermittent fasting is one of the tried and tested forms of fasting that comes packed with many health benefits (Picture Credit: Canva)
When it comes to trying out different diets to lose those extra kilos, one of the diets that is hailed and deemed to give results in no time is intermittent fasti…
Source: Moneycontrol

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are some of the health benefits associated with intermittent fasting according to recent studies?
A1: Intermittent fasting has been shown to provide several health benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. It can also lower blood pressure, reduce oxidative stress, and improve biomarkers of aging. Animal studies suggest it may help prevent cancer and improve memory and cognitive function in humans.
Q2: What are the different methods of intermittent fasting, and how do they differ?
A2: Intermittent fasting includes methods like alternate-day fasting, periodic fasting such as the 5:2 diet, and daily time-restricted eating. These methods vary in their approach to meal timing and calorie intake reduction. For instance, the 5:2 diet involves eating normally for five days and reducing calorie intake drastically for two days.
Q3: What are the potential risks or downsides of intermittent fasting?
A3: Intermittent fasting can lead to nutrient deficiencies, increased cholesterol levels, excessive hunger, irritability, headaches, and reduced adherence over time. It may also cause muscle loss and is not recommended for individuals with insulin-dependent diabetes due to potential low energy and hunger.
Q4: How does intermittent fasting impact the gut microbiome, according to recent research?
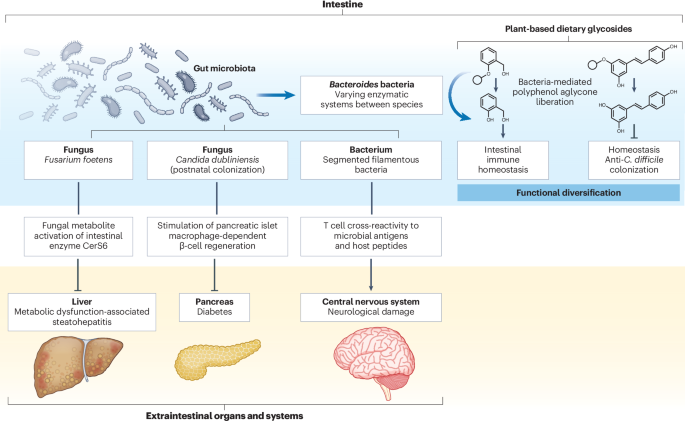
A4: Recent research indicates that intermittent fasting alters gut microbiome composition by increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria and short-chain fatty acids. This change can improve metabolic health and reduce harmful microbes. However, the effects vary based on fasting regimen and duration.
Q5: What is the stance of major health organizations on intermittent fasting?
A5: The United States National Institute on Aging and the New Zealand Ministry of Health express caution, highlighting limited and inconclusive research. While intermittent fasting may aid weight loss, they do not recommend it for everyone, particularly those with specific health conditions like insulin-dependent diabetes.
Q6: Can intermittent fasting improve cardiovascular health, and what evidence supports this claim?
A6: Yes, intermittent fasting can improve cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and improving lipid profiles. Studies have shown reductions in fasting glucose and insulin levels, leading to enhanced heart health. However, some evidence suggests potential links to increased cardiovascular risk in specific groups.
Q7: Are there any cultural or religious practices that align with intermittent fasting, and how do they compare?
A7: Yes, intermittent fasting aligns with fasting practices in religions like Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Jainism, and Judaism. These practices often involve scheduled fast days or periods of fasting, similar to the structured meal timing in intermittent fasting.
References:
- Intermittent fasting
- Dietary composition and fasting regimens differentially impact the gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acid profile in a Pakistani cohort
- Intermittent fasting: What is it and how does it work
- The Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- 10 Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- A rigorous three-month study on intermittent fasting