Summary
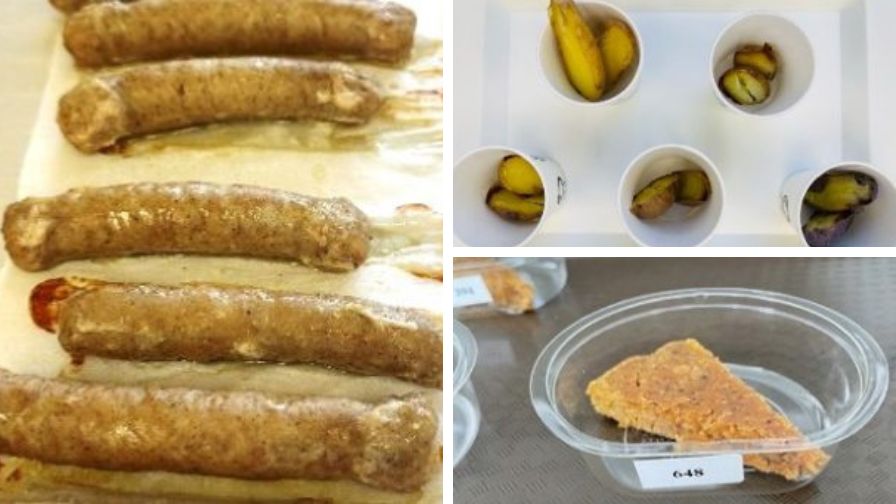
Vineland’s Consumer, Sensory and Market Insights (CSMI) team has launched several new projectsusing the new food-grade laboratory.
Source: Greenhouse Grower

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the main objectives and findings of the study on blockchain technology adoption in food bank supply chains?
A1: The study on blockchain technology adoption in food bank supply chains primarily aims to identify barriers to effective operations and explore the interrelationships among these barriers using the DEMATEL methodology. The research highlights that blockchain can enhance efficiency, transparency, and reliability in food bank supply chains, making them more sustainable. Key barriers were categorized into external and internal frameworks, and the study utilized rough theory to address subjectivity and ambiguity in expert opinions. The findings suggest that blockchain integration can significantly improve inventory tracking and compliance with food safety regulations.
Q2: How does web technology contribute to food security as seen in the government of Sri Lanka's initiatives?
A2: Web technology plays a crucial role in ensuring food security by enabling communication and resource sharing globally. The Sri Lankan government uses web technology to facilitate fair access to quality food without jeopardizing future supply. Despite its potential, the study found that existing governmental websites inadequately address food security issues. With improvements, these platforms could significantly impact food security strategies in Sri Lanka.
Q3: What insights does the survey on food computing provide regarding food data and its applications?
A3: The survey on food computing highlights the vast potential of large-scale food data to address key societal issues such as human health, behavior, and culinary culture. With the proliferation of food-related content on social and mobile networks, food computing can guide healthier lifestyles, improve health outcomes, and enrich understanding of food culture through the analysis of diverse data sources like images, recipes, and videos.
Q4: What are the potential benefits of shifting towards plant-based proteins as indicated in recent research?
A4: Recent research underscores the environmental and nutritional benefits of plant-based proteins, which are more sustainable than animal proteins. This shift can significantly reduce the climate footprint of food production. Legumes such as beans and peas are highlighted for their agronomic and nutritional advantages, offering a promising alternative to traditional protein sources like wheat and soy, which may present allergenicity challenges.
Q5: How can new food technologies in laboratories impact consumer, sensory, and market insights?
A5: Advanced food technologies in laboratories can revolutionize consumer, sensory, and market insights by enabling precise formulation and testing of food products. These innovations can lead to enhanced flavor profiles, improved nutritional content, and better alignment with consumer preferences. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, labs can generate valuable data to drive market strategies and product development.
Q6: What are the challenges and opportunities in developing superior-quality plant proteins?
A6: The development of superior-quality plant proteins faces challenges, including limited information about diverse legumes and the need for advanced technologies to enhance functional and nutritional properties. However, there are significant opportunities to explore novel protein sources, address allergenicity issues, and meet the growing demand for sustainable food options, driven by the popularity of vegetarian and vegan diets.
References:
- Blockchain Technology Adoption in Food Bank Supply Chains: A Rough DEMATEL-Based Approach
- Evaluation of the use of web technology by government of Sri Lanka to ensure food security for its citizens
- A Survey on Food Computing
- Peas (Pisum sativum subsp. arvense Asch) and Beans (Vicia faba var. minor) as Source of Quality Plant Proteins.