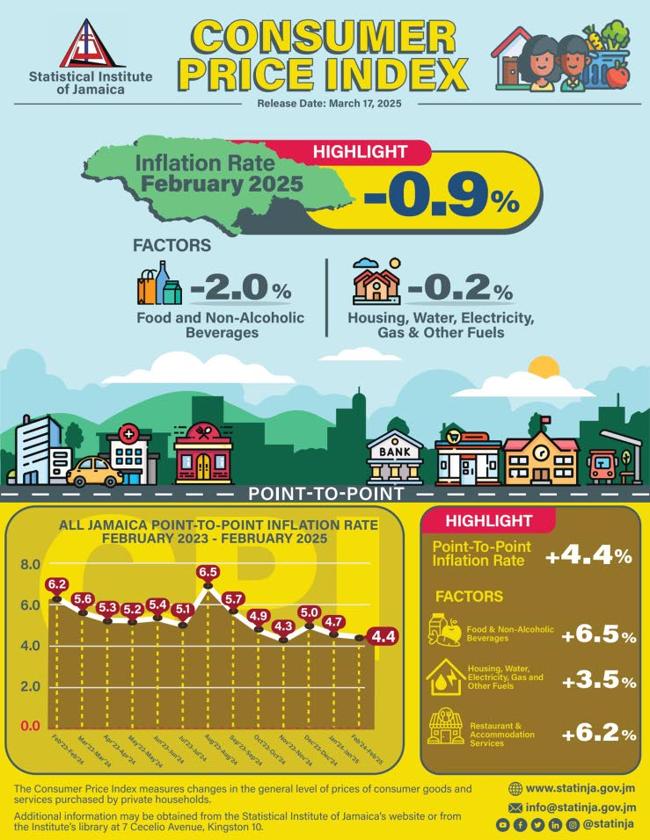
Summary
Agricultural produce prices led the decrease, with the Vegetables, Tubers, Plantains, Cooking bananas and Pulses category falling 8.8 per cent due to lower prices for items including cabbage, carrot, escallion, sweet pepper, tomato and yam.
Source: Jamaica Observer

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: How has the recent decrease in agricultural produce prices impacted inflation rates, particularly in the food sector?
A1: The recent decrease in agricultural produce prices, particularly in categories such as vegetables and tubers, has led to a reduction in food inflation. As food prices decrease, the overall inflation rate tends to drop because food expenses constitute a significant portion of consumer expenditure. This reduction is beneficial for consumers, especially those with lower incomes, as it increases their purchasing power and reduces the cost of living.
Q2: What role do subsidies and price controls play in managing food inflation?
A2: Subsidies and price controls are common policy measures used to manage food inflation. These measures help stabilize prices by reducing the cost burden on consumers. During crises such as war or famine, governments may implement food rationing and food aid programs to support lower-income individuals. Ensuring a diverse agricultural industry can also mitigate the impact of inflation on specific crops, thereby stabilizing overall food prices.
Q3: What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of moderate inflation according to economic theories?
A3: Moderate inflation can have both positive and negative effects on an economy. Positively, it can reduce unemployment due to nominal wage rigidity, encourage investment over money hoarding, and allow central banks to have greater freedom in monetary policy. However, it can also increase uncertainty over future prices, discourage savings, and potentially lead to shortages if inflation becomes too rapid. Economists often favor a low and steady rate of inflation to balance these factors.
Q4: How have machine learning algorithms been utilized in predicting agricultural commodity prices?
A4: Machine learning algorithms have shown promise in predicting agricultural commodity prices by improving accuracy and offering real-time predictions. These algorithms can handle the complex and dynamic nature of agricultural markets, assisting farmers, policymakers, and stakeholders in making informed decisions. Recent research highlights the potential of machine learning to revolutionize price prediction, though challenges remain in terms of data integration and algorithm customization.
Q5: What were the findings of the study on farmer welfare amidst food price shocks and inflation in East Java?
A5: The study conducted in East Java found that shocks to aggregate food prices could increase farmer exchange values, despite a reduction in welfare due to inflation. The research utilized a Bayesian Vector Autoregressive model to analyze the impact of food price fluctuations on farmer welfare. The findings suggest that while food price shocks can have positive effects on exchange values, inflation remains a significant concern for farmers' economic stability.
Q6: What are the main factors contributing to food inflation in India, and how can they be addressed?
A6: In India, high food inflation has been primarily driven by a mismatch in supply and demand, where agricultural production has not kept pace with rising demand. Machine learning analysis identified factors such as minimum support prices (MSP) and farm wages as significant contributors to food price changes. Addressing these issues requires policy reforms to improve agricultural productivity and ensure food security for the growing population.
Q7: How did the 2021-2023 inflation surge affect global economies, and what were its primary causes?
A7: The 2021-2023 inflation surge affected global economies by causing the highest inflation rates seen in decades. This surge was attributed to economic disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain issues, and fiscal and monetary stimuli provided during the pandemic. As economies recover, managing inflation remains critical to stabilizing markets and preventing further economic recessions.
References:
- Food inflation
- Inflation
- Predicting Agricultural Commodities Prices with Machine Learning: A Review of Current Research
- The Response of Farmer Welfares Amidst Food Prices Shock and Inflation in the Province of East Java
- Understanding food inflation in India: A Machine Learning approach