Summary
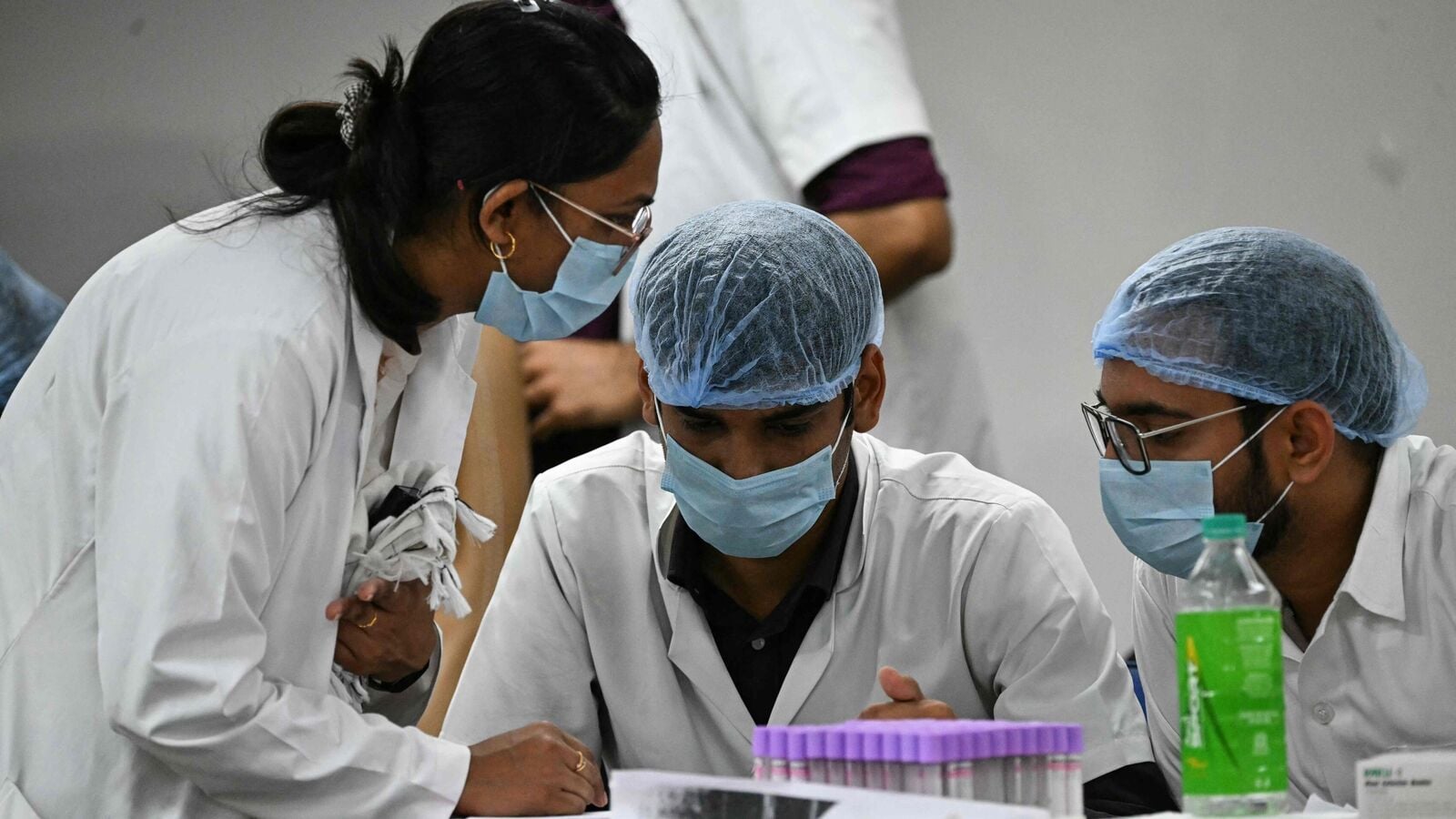
To improve Indias disaster response capacity, the government is launching a national mass casualty management training programme for over 1,000 doctors and nurses. The initiative will prepare emergency medical personnel to handle large-scale incidents.
Source: Mint on MSN.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the objective of India's national mass casualty management training program for medical staff?
A1: The objective of India's national mass casualty management training program is to enhance the country's disaster response capacity by training over 1,000 doctors and nurses. This initiative aims to prepare emergency medical personnel to efficiently handle large-scale incidents, improving the overall disaster management capabilities in various situations such as natural disasters or public health emergencies.
Q2: How does the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) contribute to disaster management in India?
A2: The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) plays a crucial role in disaster management in India by formulating policies, guidelines, and best practices. Established under the Disaster Management Act of 2005, NDMA coordinates with State Disaster Management Authorities to ensure a comprehensive and distributed approach to managing disasters across the country.
Q3: What are hospital emergency codes, and how are they used in disaster management?
A3: Hospital emergency codes are coded messages used in hospitals to alert staff about various emergencies. These codes help convey essential information quickly, minimizing misunderstanding and preventing panic among hospital visitors. In the context of disaster management, such codes can signal hospital staff to prepare for external events like natural disasters, ensuring a coordinated and efficient response.
Q4: What are some key findings from recent research on low-fidelity pediatric mass casualty incident simulations?
A4: Recent research on low-fidelity pediatric mass casualty incident simulations has shown that such simulations are effective in teaching the principles of the JumpSTART pediatric triage algorithm. Using 2D life-sized drawings, the study involved prehospital and hospital staff and demonstrated high accuracy in triage category assignments. The median time for triage completion was around 67 seconds per patient, and feedback from participants was overwhelmingly positive, highlighting the model's accessibility and effectiveness.
Q5: How does India's unique geographic and climatic conditions affect its vulnerability to natural disasters?
A5: India's geographic location below the Himalayas, its varied landscapes, and geo-climatic conditions make it particularly vulnerable to natural disasters. The country experiences monsoons, landslides, floods, droughts, cyclones, and earthquakes, with different regions facing different risks. For example, the peninsular regions are more affected by monsoons and cyclones, while the northern mountainous regions are prone to avalanches and landslides.
Q6: What are the benefits of using low-fidelity simulations for mass casualty incident training?
A6: Low-fidelity simulations for mass casualty incident training offer several benefits, including cost-effectiveness and accessibility. They allow for realistic training without the need for expensive high-fidelity simulators. Participants can engage in dynamic hands-on experiences, learning crucial triage and treatment algorithms effectively, which can be easily replicated across various environments.
Q7: What are some challenges faced by India in implementing effective disaster management strategies?
A7: Some challenges faced by India in implementing effective disaster management strategies include its vast and diverse geography, varying regional vulnerabilities, and dense population, which complicate coordinated responses. Additionally, the need for comprehensive training and resources, like the mass casualty management training program, highlights the ongoing need to enhance disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
References:
- Disaster management in India
- Low-Fidelity, In Situ, Accessible Pediatric Mass Casualty Incident Simulation to Evaluate and Improve Pediatric Readiness
- National Disaster Management Authority (India)
- Hospital emergency codes