Summary
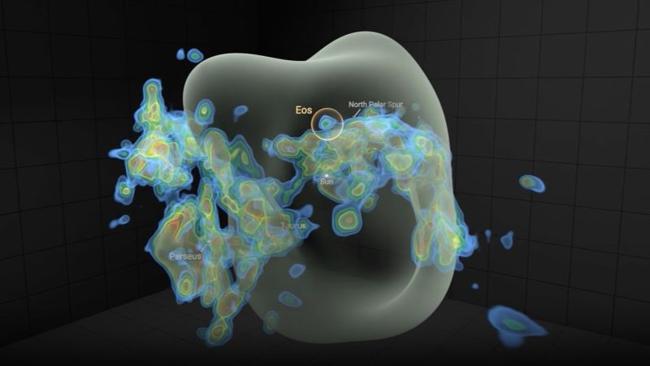
Named Eos, the cloud of gas would appear huge in the night sky if visible to the naked eye and could shed light on solar system formation.
Source: CNN on MSN.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the significance of the newly discovered star-forming cloud named Eos?
A1: The discovery of the star-forming cloud named Eos is significant as it offers insights into the processes of star and solar system formation. This cloud, located in our cosmic neighborhood, could shed light on the conditions that prevailed during the formation of our solar system. Understanding these conditions helps astronomers and cosmologists trace the evolutionary history of the solar system and possibly predict the future dynamics of similar star systems.
Q2: How do the properties of Eos compare to other known star-forming regions?
A2: Eos is a massive cloud of gas that, if visible, would appear enormous in the night sky. Compared to other known star-forming regions, Eos's characteristics could provide unique data on its composition, size, and the types of stars it might form. This comparison is crucial for astronomers to understand the diversity in star formation processes across different regions in space.
Q3: What are the potential implications of Eos on our understanding of solar system formation?
A3: The potential implications of Eos on our understanding of solar system formation include insights into the initial conditions that lead to the birth of stars and planets. By studying Eos, scientists can compare its properties with theoretical models of solar system formation, refining our knowledge of how stars like the Sun and planetary systems like ours come into existence.
Q4: What recent advancements have been made in the study of star-forming clouds similar to Eos?
A4: Recent advancements in the study of star-forming clouds include the development of more sophisticated models that simulate the conditions within these clouds. Researchers have been able to better understand the chemical composition and dynamics of these regions, thanks to improved observational data from telescopes and enhanced computational models. These advancements help in predicting the types of stars and potential planetary systems that may form within such clouds.
Q5: How might the study of Eos contribute to our knowledge of cloud formation in substellar atmospheres?
A5: Studying Eos can enhance our understanding of cloud formation in substellar atmospheres by providing real-world data that can be compared with models of cloud formation in brown dwarfs and exoplanet atmospheres. Insights from Eos can help in refining these models, particularly in understanding the interactions between different elements and the conditions that lead to cloud formation in such environments.
Q6: In what ways could the chemical composition of Eos influence future research in astronomy and cosmochemistry?
A6: The chemical composition of Eos could provide critical data for future research in astronomy and cosmochemistry by offering a reference point for the elemental abundances present in early star-forming regions. This information could be used to model the collapse of molecular clouds and the subsequent formation of stars and planetary systems, aiding in the development of more accurate cosmochemical models.
Q7: What are the challenges faced by astronomers in observing and analyzing star-forming clouds like Eos?
A7: Astronomers face several challenges in observing and analyzing star-forming clouds like Eos, including their vast distances, which make detailed observations difficult. The complexity of these clouds, with their varying densities and compositions, also poses a challenge in developing accurate models. Additionally, the need for high-resolution data that can only be captured by advanced telescopes limits the frequency and scope of observations.
References:
- Cloud formation in substellar atmospheres
- Solar Elemental Abundances