Summary
Matchas popularity has skyrocketed in recent years, making it difficult for Japanese producers to meet the global demand. To maintain a steady supply, some have begun blending first-harvest matcha (ichibancha), which has a superior quality, with lower-quality grades. This is exactly why, if youre …
Source: Chowhound

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the characteristics of high-quality matcha and how can consumers identify them?
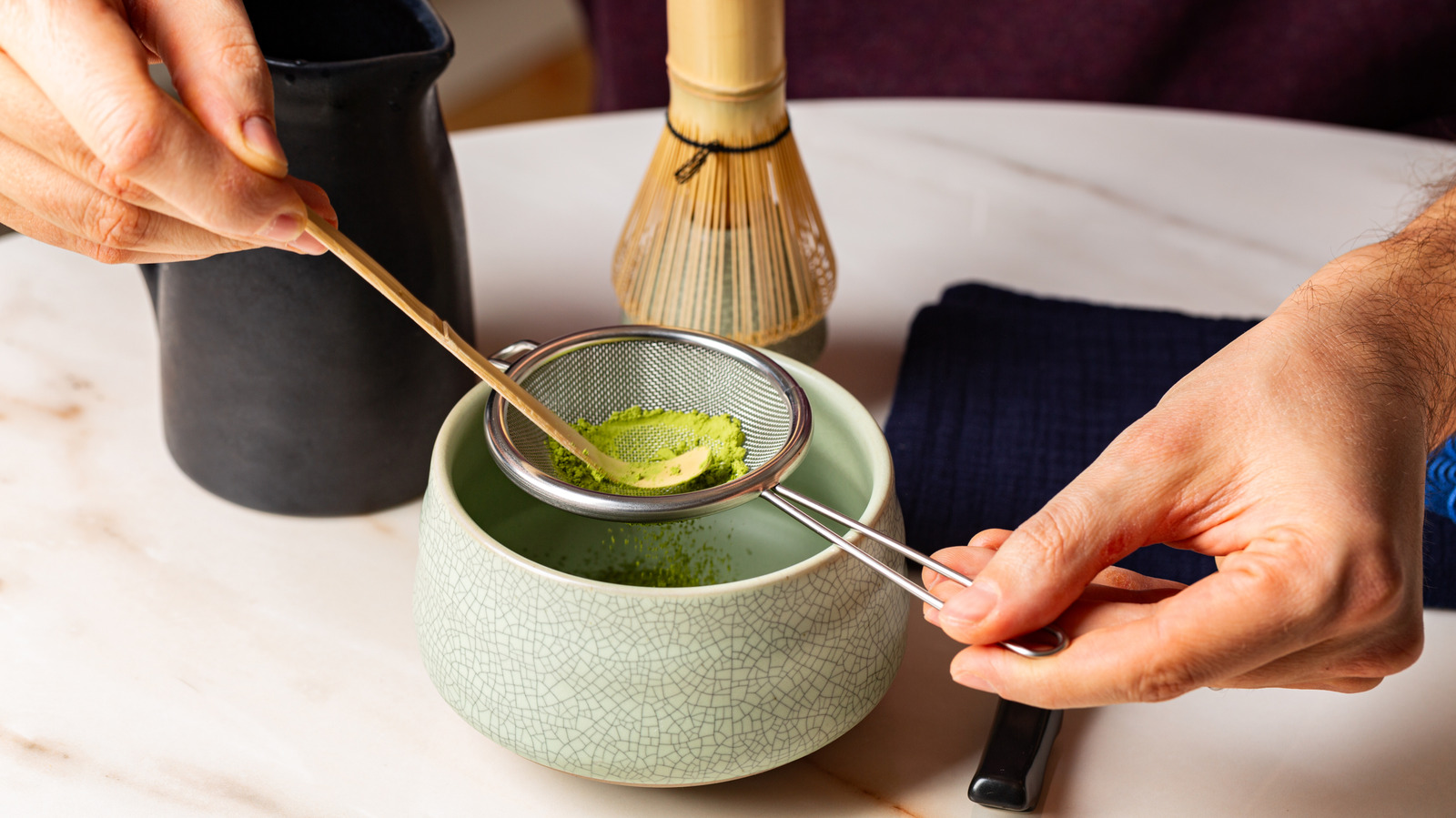
A1: High-quality matcha is characterized by its vibrant, bright green color, which indicates proper shading of tea leaves before harvest. The texture should be fine and smooth, similar to baby powder, and it should dissolve easily in water, resulting in a creamy and frothy tea. The aroma should be fresh, grassy, and slightly sweet, reminiscent of freshly cut grass. Finally, high-quality matcha has a rich umami flavor with a complex, sweet, and vegetal taste. Consumers can use the finger test by pressing the powder and observing the smoothness and continuity of the line drawn to assess quality.
Q2: How has the global demand for matcha impacted its production and market dynamics in recent years?
A2: The global demand for matcha has significantly increased, leading to a surge in production. Japan, the leading producer, saw its matcha production nearly triple from 1,471 tons in 2010 to 4,176 tons in 2023. Despite this, demand continues to outstrip supply, driven by its health benefits and use in various culinary and skincare applications. The matcha market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 7.1 billion by 2033. This rising demand has resulted in higher prices and a potential shortage as production capacities are stretched.
Q3: What are the health benefits of matcha according to recent scientific studies?
A3: Recent scientific studies highlight matcha's health benefits, particularly its high levels of catechins and polyphenols, which combat inflammation and oxidative stress. Matcha's bioactive compounds, like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and L-theanine, have been linked to improved cognition, mood, and neuroprotection. Studies suggest that matcha may enhance cognitive function and sleep quality, making it a popular choice for those seeking functional, health-promoting beverages.
Q4: How does the shading process impact the quality and characteristics of matcha?
A4: The shading process is crucial for high-quality matcha as it increases chlorophyll production, resulting in the powder's vibrant green color and strong umami flavor. By shading tea leaves for several weeks before harvest, the process elevates the concentration of amino acids, particularly L-theanine, enhancing the tea's sweet and mellow taste. This method, developed during Japan's Muromachi period, remains vital for producing the finest matcha, especially for ceremonial-grade tea.
Q5: What are the implications of synthetic food ingredients on health based on recent research?
A5: Recent research has raised concerns about the health impacts of synthetic food ingredients. Studies indicate that these ingredients can contribute to various health issues, including allergies and metabolic disorders. The increasing preference for natural and organic products, such as matcha, reflects a growing consumer awareness of potential risks associated with synthetic additives, prompting a shift towards more natural, health-conscious consumption.
Q6: What role does matcha play in the cultural and culinary traditions of Japan?
A6: Matcha plays a significant role in Japanese cultural and culinary traditions, particularly in the traditional tea ceremony known as chanoyu. This meditative practice emphasizes the preparation, serving, and consumption of matcha as a symbol of hospitality and mindfulness. Beyond cultural ceremonies, matcha is widely used to flavor foods like mochi, soba noodles, and green tea ice cream, showcasing its versatility and deep-rooted significance in Japanese cuisine.
Q7: How has the matcha market adapted to the challenges of climate and agricultural changes?
A7: The matcha market has faced challenges due to climate changes, such as heatwaves impacting crop yields. In response, producers have implemented more efficient agricultural practices and diversified their product offerings to meet demand. Despite these efforts, the market continues to grapple with potential shortages and price increases as production capacities are tested by environmental factors and rising global demand.