Summary
We usually think of bacteria as bad guys, malicious microbes whose only goal is to spread illness, but thats only part of the story. In reality, we rely on bacteria for our survival.
The gut microbiome is filled with a wide variety of germs, most of which are beneficial. They help break down our f…
Source: SYFY

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the role of the gut microbiome in human health?
A1: The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, residing in the digestive tract. It plays a vital role in various bodily functions, such as metabolizing dietary compounds, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, and modulating the immune response. The gut microbiome also influences behavior through the gut-brain axis and is involved in colonization resistance against pathogens.
Q2: How can gut microbiota-derived metabolites impact cancer development?
A2: Gut microbiota-derived metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids, indoles, and organic acids, are crucial for host physiology and can influence cancer development. These metabolites can modulate immune function, inflammation, and even cell proliferation, which are key factors in the progression of certain cancers, including colorectal cancer.
Q3: What recent advancements have been made in analyzing the gut microbiome's impact on cancer?
A3: Recent studies have utilized advanced methodologies like single-cell sequencing and spatial technologies to unravel the complex composition of the gut microbiome's role in colorectal cancer. These studies highlight the microbiome's influence on tumor development and progression, suggesting potential therapeutic targets.
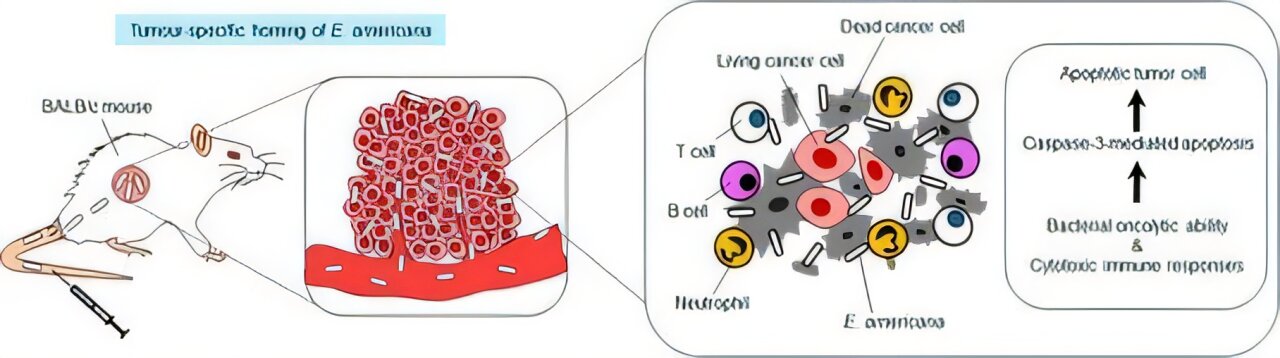
Q4: What potential does reptile and amphibian bacteria hold in cancer treatment?
A4: Reptile and amphibian bacteria are being explored for their unique antimicrobial properties, which may offer novel approaches in cancer treatment. These bacteria can produce bioactive compounds with potential antitumor effects, offering a new avenue for developing cancer therapeutics.
Q5: How are AI technologies enhancing cancer prognosis and treatment strategies?
A5: AI technologies, including machine learning and deep learning algorithms, have significantly advanced cancer prognosis by analyzing complex multi-omics data. These technologies improve survival prediction accuracy, enabling clinicians to tailor personalized treatment strategies, especially in cancers like Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).
Q6: What are the challenges in identifying molecular signatures across different cancer types?
A6: Identifying molecular signatures across various cancer types is challenging due to the diverse biological mechanisms involved in cancer progression. However, recent computational data mining efforts have identified 18 pan-cancer molecular signatures, suggesting potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Q7: How do statistical methods contribute to microbiome analysis?
A7: Statistical methods are essential in microbiome analysis as they help decode the complex data generated from microbiome studies. These methods enable researchers to understand the interactions between microbiomes and their hosts, offering insights into their roles in health and disease.
References:
- Gut microbiota - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gut_microbiota
- Development of a GC-MS/MS method to quantify 120 gut microbiota-derived metabolites - Arxiv
- Intratumoral microbiome: a crucial regulating factor in development and progression of colorectal cancer - Arxiv
- AI-Enabled Lung Cancer Prognosis - Arxiv
- Multi-cancer molecular signatures and their interrelationships - Arxiv
- Statistical Methods for Microbiome Analysis: A brief review - Arxiv