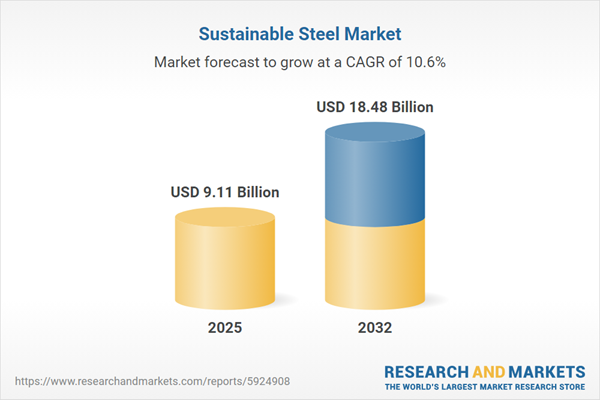
Summary
Advertisement
Holcim Germany and the A&S Detmering Group have entered into a strategic partnership to strengthen the circular economy within the building materials sector across the metropolitan regions of Hanover, Braunschweig, Gttingen, Wolfsburg and beyond.
As part of the agreement, Holcim wil…
Source: International Cement Review

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the strategic purpose behind Holcim Germany's partnership with A&S Detmering Group in the context of the circular economy?
A1: Holcim Germany and A&S Detmering Group have partnered strategically to enhance the circular economy within the building materials sector in regions like Hanover, Braunschweig, Göttingen, and Wolfsburg. The partnership aims to strengthen material recycling processes, with Holcim acquiring shares in A&S Detmering’s recycling and demolition business. This move secures access to high-quality demolition materials and expands Holcim's processing capacities, furthering sustainable material recovery and reuse initiatives.
Q2: How does the concept of a circular economy differ from a traditional linear economy, and what are its potential global benefits?
A2: A circular economy emphasizes the reuse, recycling, and refurbishment of products to extend their lifecycle, unlike the traditional linear model of make-use-dispose. This approach reduces waste, lowers pollution, and regenerates natural systems. Globally, adopting circular economy principles could cut emissions significantly, potentially reducing them by 22.8 billion tons, or 39% of global emissions in 2019.
Q3: What role does blockchain technology play in advancing circular economy models, according to recent scholarly research?
A3: Blockchain technology is pivotal in transitioning to circular economy models by providing transparent and secure supply chain management. It enhances product accountability and traceability, although scalability, interoperability, and regulatory challenges remain. Continued research and stakeholder engagement are crucial to overcoming these hurdles and fully leveraging blockchain's potential in circular economy frameworks.
Q4: What types of business models support the transition to a circular economy, and how do they contribute to sustainability?
A4: Circular business models such as product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, and life extension models optimize resource use and reduce waste. These models create value for businesses and consumers while contributing to sustainability goals by keeping products and materials in continuous circulation, thus supporting the circular economy's principles of designing out waste and regenerating natural systems.
Q5: In what ways is Holcim Germany integrating circular economy practices in its operations, particularly regarding wind turbine materials?
A5: Holcim Germany collaborates with GE Renewable Energy to explore recycling solutions for decommissioned wind turbines. They aim to use wind blade materials in constructing new wind farms, leveraging Holcim's experience in energy recovery from wind blades. This initiative aligns with Holcim’s strategy to promote sustainability and expand circular solutions, particularly in the European market.
Q6: What are the economic implications of transitioning to a circular economy for businesses and global markets?
A6: Transitioning to a circular economy can lead to significant economic benefits, including material cost savings estimated at over one trillion dollars globally. It enhances resource productivity, reduces commodity price volatility, and fosters sustainable growth. This shift decouples economic activity from finite resource consumption, offering resilience and competitive advantages in global markets.
Q7: How does the partnership between Holcim Germany and A&S Detmering Group impact local demolition and recycling operations?
A7: The partnership allows Holcim to integrate A&S Detmering's recycling hubs into its operations, transforming them into Holcim ECOCycle® Centres. This enhances local demolition and recycling capabilities, supporting sustainable construction practices by improving material recovery and reuse in the metropolitan regions of Hanover, Braunschweig, Göttingen, and Wolfsburg.
References:
- A Systematic Literature Review on the Use of Blockchain Technology in Transition to a Circular Economy