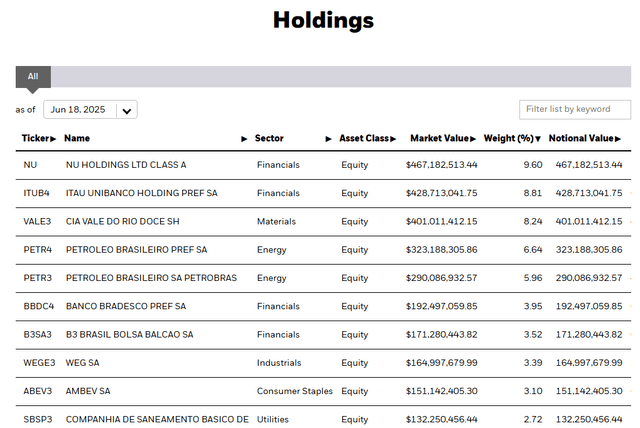
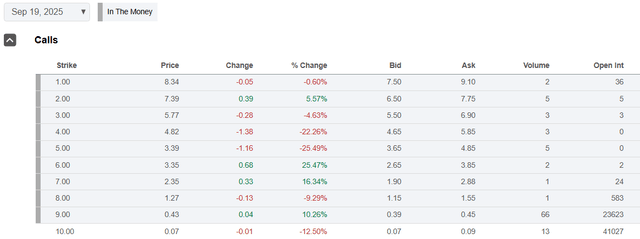
Summary
The Brazilian Central Bank raised the interest rate by 0.25% to 15% on June 18, the highest level since 2006. The reasons for the increase were the uncertain global scenario and inflation outside the target. It is worth remembering that the inflation target is 3% with a 1.5% tolerance, and inflation is currently 5.32% in Brazil.
Source: Seeking Alpha

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What were the main reasons for the Brazilian Central Bank to raise interest rates to 15% in June 2023?
A1: The Brazilian Central Bank increased the interest rate to 15% primarily due to an uncertain global scenario and inflation rates that exceeded the target. The inflation target was set at 3% with a 1.5% tolerance, but the actual inflation rate was at 5.32%.
Q2: How does Brazil's current interest rate compare historically?
A2: Brazil's interest rate of 15% as of June 2023 is the highest since 2006. This decision reflects the central bank's aggressive stance to control inflation and stabilize the economy in a challenging global financial climate.
Q3: What impact do interest rate hikes typically have on the stock market, specifically in Brazil?
A3: Interest rate hikes generally lead to higher borrowing costs, which can reduce consumer spending and corporate investments, potentially slowing down economic growth. However, in Brazil, despite the rate hike, stock markets have seen a rise, possibly due to investor confidence in the central bank's measures to control inflation and stabilize the economy.
Q4: How does the increase in interest rates affect consumer behavior and economic growth in Brazil?
A4: Higher interest rates often lead to decreased consumer spending as loans and credit become more expensive. This can slow economic growth as businesses experience reduced demand for goods and services, and investment in expansion may decline.
Q5: What are the potential long-term effects of sustained high-interest rates on Brazil's economy?
A5: Sustained high-interest rates can lead to reduced economic growth, as borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially slowing investment and consumer spending. However, if managed well, it can also lead to controlled inflation and a more stable economic environment.
Q6: In what ways are Brazilian stocks showing resilience despite high-interest rates?
A6: Brazilian stocks might be showing resilience due to investor confidence in the central bank's actions to curb inflation and stabilize the economy. Additionally, sectors less sensitive to interest rate changes or those benefiting from global economic trends may contribute to stock market stability.
Q7: Are there any scholarly insights on how interest rate hikes impact market dynamics, specifically in emerging markets like Brazil?
A7: Scholarly articles suggest that interest rate hikes in emerging markets can lead to capital outflows, currency depreciation, and increased borrowing costs. However, effective policy measures and investor confidence in economic management can mitigate these effects, as seen in Brazil's recent market performance.
References:
- List of sovereign states by central bank interest rates
- Deindustrialization of Brazil
- Optimal Market Making in the Chinese Stock Market: A Stochastic Control and Scenario Analysis
- Published: 2023-06-05
- Contagion Effects of the Silicon Valley Bank Run
- Published: 2024-05-10
- Published: 2023-11-26