Summary
April 21, 2025. More for You. El Salvador’s Bukele proposes prisoner swap with Venezue
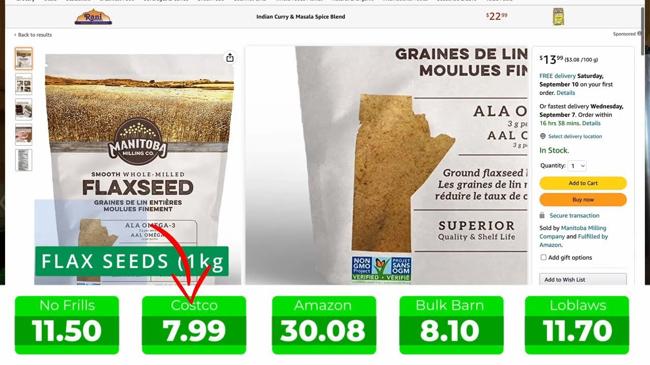
Source: stelleandcobakes on MSN.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the key health benefits and potential risks associated with adopting a vegan diet?
A1: A vegan diet, which excludes all animal products, is associated with several health benefits including lower levels of inflammation and oxidative stress due to its richness in phytonutrients and antioxidants. These factors are linked to a reduced risk of systemic inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. However, potential risks include deficiencies in critical nutrients such as vitamin B12, DHA, EPA, and iron, which can lead to cognitive decline and mood disturbances if not properly managed.
Q2: How has interest in veganism evolved over the past decade?
A2: Interest in veganism has significantly increased since the 2010s, driven by ethical, environmental, and health considerations. The movement, which promotes abstaining from animal products, has gained momentum due to growing awareness about the commodity status of animals and the ecological impact of animal agriculture.
Q3: What are the latest developments in plant-based diets according to recent scholarly articles?
A3: Recent studies highlight the economic and nutritional implications of least-cost diets, emphasizing optimization and consumer behavior. These diets focus on nutrient adequacy at the lowest cost, showing a relationship between cost minimization and utility maximization, relevant to ongoing debates about the affordability of healthy diets worldwide.
Q4: What role do vegan and vegetarian diets play in neurological health?
A4: Vegan and vegetarian diets can benefit neurological health when well-planned, as they are rich in phytonutrients and antioxidants that reduce inflammatory markers. However, they may also pose risks for neurological health due to potential deficiencies in nutrients like vitamin B12, DHA, EPA, and iron, which are crucial for cognitive function.
Q5: How do high-fat diets impact breast cancer treatment according to recent research?
A5: Recent research using mathematical models of mouse experiments suggests that high-fat diets negatively impact the efficacy of anti-hormonal treatments for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. The findings emphasize the importance of considering diet and obesity as factors influencing treatment outcomes.
Q6: What are some common misconceptions about vegan diets?
A6: Common misconceptions about vegan diets include the belief that they are inherently deficient in protein and essential nutrients. While it is true that certain nutrients like vitamin B12 are less prevalent in plant-based foods, these diets can be nutritionally adequate if carefully planned to include fortified foods or supplements.
Q7: What are some recent consumer trends in plant-based food products?
A7: Recent consumer trends indicate a growing demand for plant-based food products, driven by an increase in health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers. Innovations in plant-based foods include meat and dairy alternatives that cater to taste and texture preferences, aiming to provide viable options for traditional animal products.
References:
- Plant-based diet - Wikipedia
- Veganism - Wikipedia
- Impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Diets on Neurological Health: A Critical Review
- Least-cost diets to teach optimization and consumer behavior, with applications to health equity, poverty measurement and international development
- Modeling of mouse experiments suggests that optimal anti-hormonal treatment for breast cancer is diet-dependent