Summary
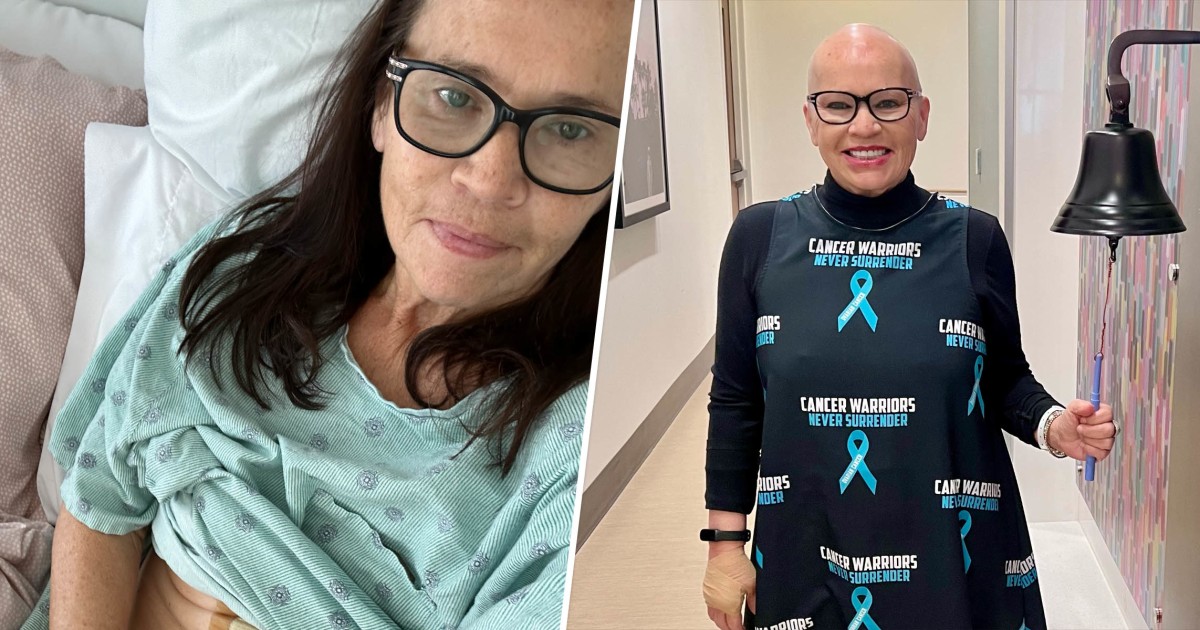
A COUPLE originally from Colchester have faced adversity due to two world changing diagnoses including cancer and the discovery of a brain tumour.
Source: The Gazette

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What are the primary causes of brain tumors, and how do they differ from secondary brain tumors?
A1: Brain tumors can be classified into primary and secondary tumors. Primary brain tumors originate in the brain and include types like meningiomas and astrocytomas such as glioblastomas. Secondary or metastatic brain tumors are more common and occur when cancer spreads to the brain from other parts of the body, like the lungs. The causes of most brain tumors are unknown, but factors like ionizing radiation, certain viruses, and genetic syndromes may increase risk. Secondary brain tumors are often linked to cancers like lung cancer.
Q2: What advancements in glioblastoma treatment have been noted in recent studies?
A2: Recent studies have focused on the purinergic receptor P2X7 (P2X7R) in glioblastoma, the most aggressive form of primary brain cancer. Inhibition of P2X7R with a pharmacological antagonist has shown promising results, significantly decreasing tumor cell numbers and increasing cell death, without affecting apoptosis pathways. These findings suggest potential for new therapeutic strategies focusing on cell signaling pathways in glioblastoma treatment.
Q3: How does early diagnosis impact the survival rates of brain tumor patients?
A3: Early diagnosis of brain tumors is crucial as it influences treatment options and survival rates. Diagnosis typically involves medical examinations, CT scans, and MRIs, followed by biopsies. For malignant brain tumors, the five-year survival rate in the United States is approximately 33%, but it varies significantly based on tumor type and stage at diagnosis. Early detection can enable timely interventions and improve outcomes.
Q4: What are the common symptoms of brain tumors, and how might they vary?
A4: Symptoms of brain tumors depend on the tumor's size and location within the brain. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, visual disturbances, vomiting, and mental changes. Other symptoms might include difficulty walking, speaking, sensory issues, or loss of consciousness. These symptoms result from the tumor pressing on or affecting different parts of the brain.
Q5: How do lifestyle factors influence the risk of developing cancer?
A5: Lifestyle factors significantly impact cancer risk. Tobacco and alcohol use, obesity, and a diet low in fruits and vegetables are major contributors, accounting for about 33% of cancer deaths. Physical inactivity, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants also increase risk. Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and minimizing tobacco and alcohol use.
Q6: What role do infections play in cancer development?
A6: Infections are responsible for approximately 16-18% of cancers globally. Viruses like hepatitis B and C, HPV, and Epstein-Barr virus, along with certain bacteria and parasites, can lead to cancer by altering cellular genetics. Vaccination against hepatitis B and HPV has been effective in significantly reducing cancer risks associated with these infections.
Q7: What are the most common types of cancer in children, and how do they differ from adult cancers?
A7: In children, the most common cancers are acute lymphoblastic leukemia and brain tumors, while in adults, lung, prostate, and breast cancers are prevalent. The causes and types of cancers in children often differ from adults, with genetic factors playing a more significant role in pediatric cancers. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in improving survival rates in children.
References:
- Brain tumor - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_tumor
- Cancer - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer
- Purinergic P2X receptor 7 (P2X7R) inhibition induced cytotoxicity in glioblastoma - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4567890/