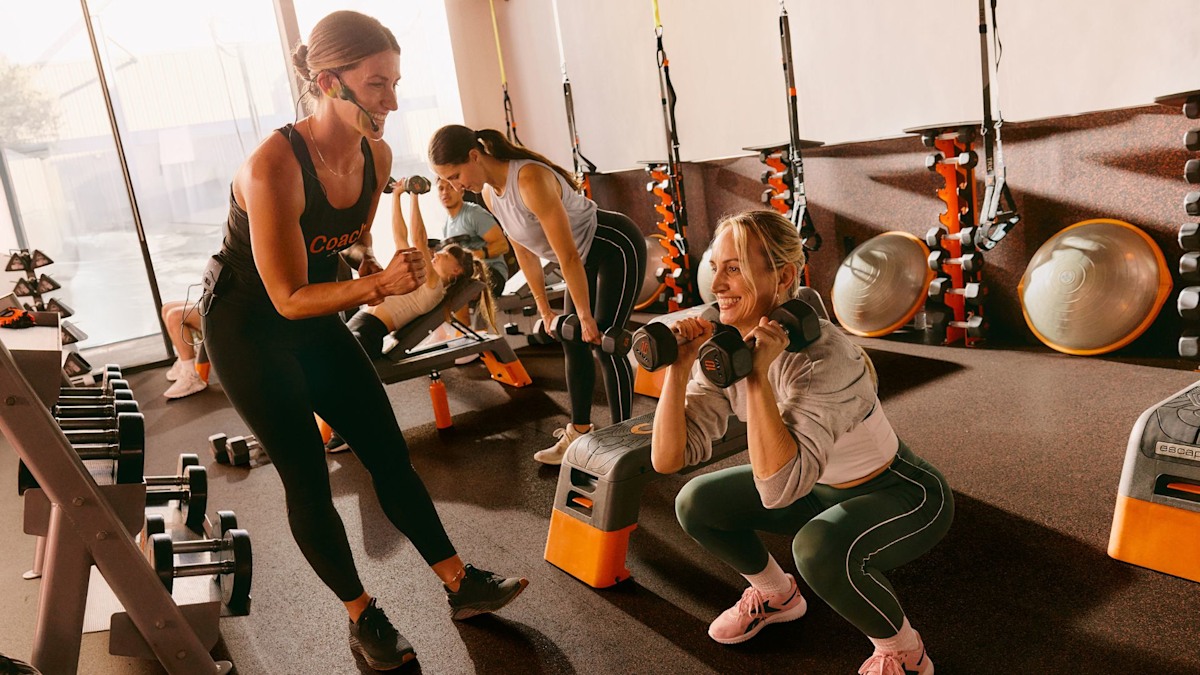Summary
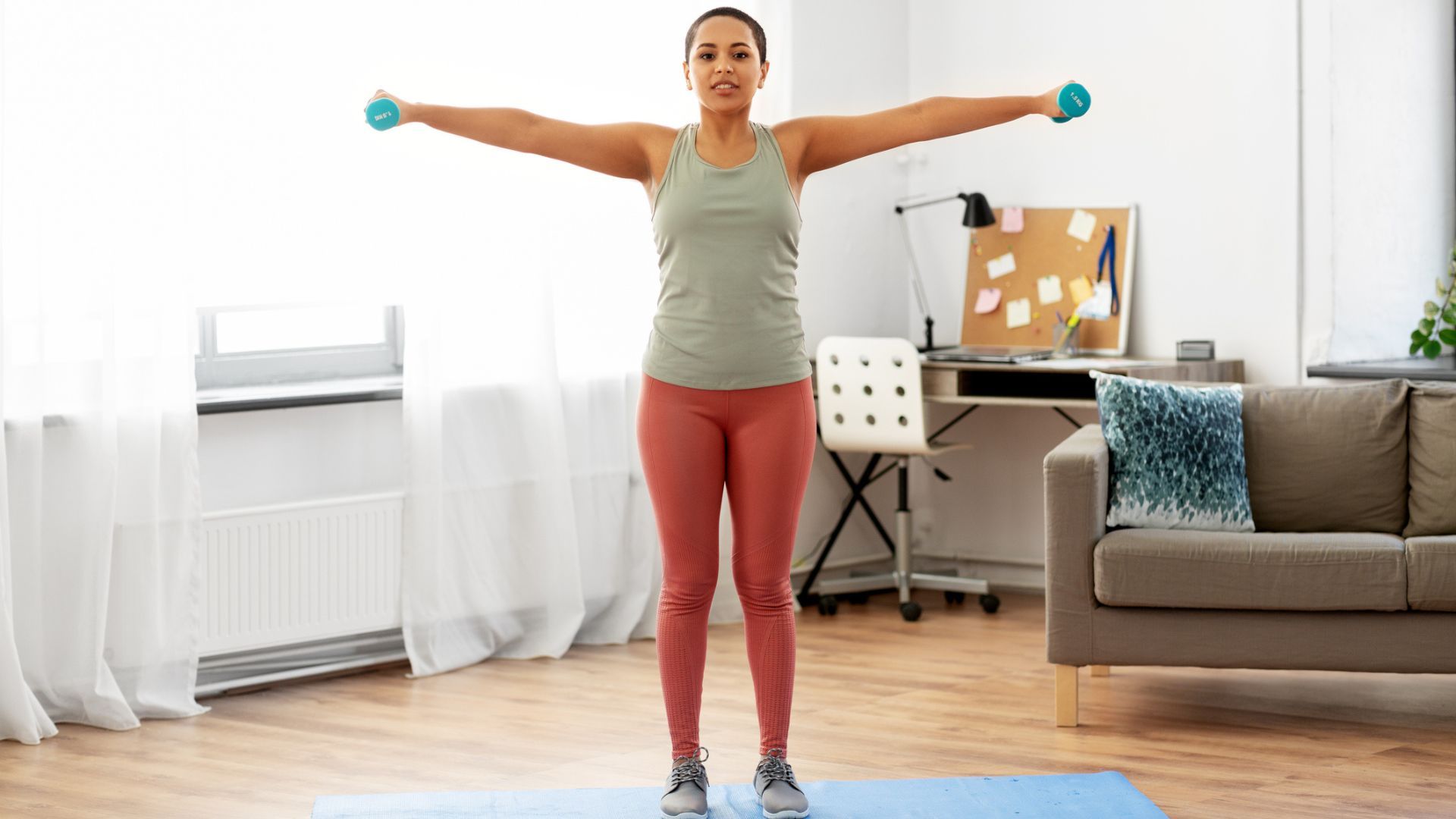
Upper-body workouts are about more than toning your arms. They help build strength and mobility, so you can move more easily throughout your day.
Upper-body circuits reinforce healthy shoulder mobility, improve posture and strengthen through positions you use in daily lifelifting, reaching, pushi…
Source: Fit&Well

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: How do upper-body workouts contribute to improved posture and mobility?
A1: Upper-body workouts enhance shoulder mobility, strengthen muscles used in daily activities like lifting and reaching, and promote better posture by reinforcing the alignment of the spine. Regular upper-body exercises can also prevent muscle imbalances that contribute to poor posture.
Q2: What are some effective upper-body exercises that can be performed without equipment?
A2: Calisthenics exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, and planks effectively build upper-body strength without equipment. These exercises use body weight as resistance, promoting strength, stability, and coordination by engaging multiple joints simultaneously.
Q3: What are the health benefits of incorporating strength training into a fitness routine?
A3: Strength training increases muscle, tendon, and ligament strength, improves bone density and metabolism, enhances joint and cardiac function, and reduces injury risk. It is beneficial for athletes and the elderly as part of their training regimen to improve overall health and performance.
Q4: What does the latest research say about upper-body exercises for older adults?
A4: A study on the Mobility-Fit program, focusing on upper-limb strength among older adults, showed superior improvements in elbow extension strength and quality of life. The program included agility, balance, and resistance exercises, demonstrating significant benefits for older adults in long-term care facilities.
Q5: How does strength training differ from other forms of exercise in terms of intensity and goals?
A5: Strength training, also known as resistance training, is anaerobic, focusing on progressively increasing muscle force output. It aims to improve physical strength and is distinct from aerobic exercises, which primarily enhance cardiovascular endurance.
Q6: Can short-duration exercises be effective for improving health and posture?
A6: Yes, even short-duration exercises, like a five-minute upper-body workout, can significantly improve posture and health. Regular, brief workouts contribute to muscle strength and mobility, reducing the risk of health issues without requiring extensive time commitments.
Q7: What role does posture play in overall health and daily functioning?
A7: Good posture is crucial for maintaining balance, preventing back and neck pain, and ensuring efficient movement. It affects breathing, digestion, and the ability to perform daily activities comfortably and efficiently, highlighting the importance of exercises that promote proper posture.
References:
- Exercise - Wikipedia
- Strength training - Wikipedia
- Calisthenics - Wikipedia
- Effects of Mobility-Fit, a tailored multicomponent physical activity program with upper-limb emphasis, on strength, mobility and fall risk among older adults in long-term care: a cluster randomised controlled trial.