Summary
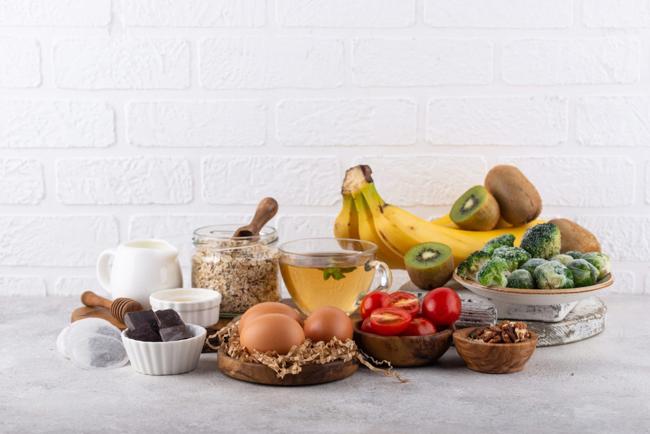
Discover 9 unexpected tryptophan-rich foods beyond turkey that can naturally enhance your mood, improve sleep quality, and boost overall brain health.
Source: Rolling Out

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is tryptophan, and why is it important for mood and brain health?
A1: Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that humans must obtain through their diet. It serves as a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, and melatonin, a hormone that controls sleep-wake cycles. By influencing serotonin and melatonin production, adequate tryptophan intake is linked to improved mood, better sleep quality, and overall brain health.
Q2: Which nine tryptophan-rich foods, apart from turkey, are recognized for potentially boosting mood and supporting a nutritional diet?
A2: In addition to turkey, nine tryptophan-rich foods include eggs, cheese, salmon, tofu, nuts and seeds (like pumpkin seeds), soy products, oats, bananas, and chicken. These foods offer significant amounts of tryptophan and provide other essential nutrients that support a balanced nutritional diet.
Q3: How does tryptophan intake influence sleep quality according to recent nutritional research?
A3: Research shows that tryptophan increases melatonin synthesis, which promotes healthy sleep cycles. Consuming tryptophan-rich foods, especially in the evening, can aid in falling asleep faster and improving sleep quality. However, excessive supplementation has been linked to rare health risks, so moderation through diet is recommended.
Q4: What are the recommended dietary guidelines for tryptophan intake to maintain balanced nutrition in adults?
A4: International dietary guidelines suggest that adults should consume approximately 4 mg of tryptophan per kilogram of body weight daily. This requirement can typically be met through a diet that includes protein-rich foods like dairy, eggs, fish, and plant-based sources such as legumes and seeds, supporting overall balanced nutrition.
Q5: What did the 2018 study on vegetarian diets reveal about sources of essential amino acids, like tryptophan, for those following plant-based nutrition?
A5: The 2018 study on vegetarian diets identified that foods such as immature lima beans and mushrooms are excellent plant-based sources of essential amino acids, including tryptophan. The research emphasized the importance of a varied diet to ensure adequate intake of all essential nutrients, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
Q6: How are modern technologies like smart healthcare and computer vision improving the tracking of nutritional intake, especially for amino acids like tryptophan?
A6: Recent advancements such as NutriVision use smartphone-based image capture and deep learning algorithms to identify foods, estimate portion sizes, and provide detailed nutritional breakdowns, including tryptophan content. This technology enhances diet management by allowing users to monitor their intake of essential nutrients in real time, supporting healthier dietary choices.
Q7: What potential health risks are associated with excessive tryptophan supplementation, and how can these be avoided in a nutritional diet?
A7: Excessive tryptophan supplementation has been linked to eosinophilia–myalgia syndrome, a rare but serious neurological condition. To avoid such risks, experts recommend obtaining tryptophan from natural food sources within a balanced diet, rather than high-dose supplements, in line with nutritional safety guidelines.
References:
- Tryptophan - Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tryptophan
- Diet (nutrition) - Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diet_(nutrition)
- Healthy diet - Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Healthy_diet
- Eosinophilia–myalgia syndrome - Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eosinophilia%E2%80%93myalgia_syndrome