Summary
United States Circular Economy Market Share Booms | Top 5 Companies – Waste Management, Inc., Umicore, Covestro AG, Paprec Group, Stora Enso Oyj
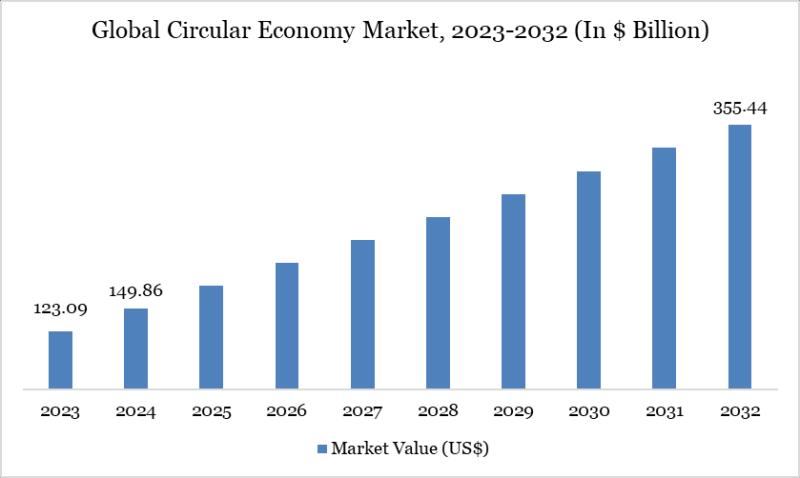
Circular Economy Market
https://www.datamintelligence.com/download-sample/circular-economy-market?kb
https://www.datamintelligence.com/buy-now-page?repo…
Source: openPR.com

AI News Q&A (Free Content)
Q1: What is the concept of a circular economy and how does it differ from a traditional linear economy?
A1: A circular economy (CE) is a model of resource production and consumption that emphasizes sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials for as long as possible. Unlike a traditional linear economy, which follows a 'take-make-dispose' model, the circular economy aims to design out waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use, and regenerate natural systems, ultimately reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
Q2: How has the circular economy concept been adopted in the United States?
A2: In the United States, the circular economy concept has gained traction as a means to minimize carbon emissions and raw material consumption, open new market opportunities, and enhance sustainability. It is seen as a strategy for long-term growth, and businesses are encouraged to adopt circular business models that focus on product life extension, sharing platforms, and product-as-a-service models.
Q3: What role do business models play in enabling the shift to a circular economy?
A3: Business models are crucial in the transition to a circular economy. They include strategies such as product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, and product life extension, which optimize resource utilization and reduce waste. These models help businesses and customers create value while adhering to the circular economy's principles of sustainability.
Q4: What are some environmental benefits associated with the global implementation of circular economy strategies?
A4: Globally implementing circular economy strategies can significantly reduce emissions. For instance, in sectors like cement, aluminum, steel, plastics, and food, emissions could be reduced by 9.3 billion metric tons of CO2 equivalent, equating to all current emissions from transportation. This approach contributes to tackling climate change and reducing pollution and biodiversity loss.
Q5: What are the latest scholarly findings on the impact of market power in the United States?
A5: Recent scholarly research indicates that market power in the United States has steadily increased since 1970, with the aggregate markup rising from 10% over marginal cost to 23% by 2020. While market power indicators have increased, the profit share has remained constant at 18% of GDP due to rising fixed costs and changes in technology. These findings suggest that aggressive antitrust law enforcement could reduce firm dynamism and competition.
Q6: How does the circular economy aim to connect actors and resources at a regional level?
A6: The circular economy aims to geographically connect actors and resources to close material loops at a regional level. This involves creating networks that facilitate the sharing, leasing, and recycling of materials, thereby reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency at a local scale, contributing to regional sustainability goals.
Q7: What are the challenges faced by developing economies in adopting circular economy principles?
A7: Developing economies face challenges such as a concentration of employment in low-skill occupations and jobs with high automation potential, compounded by lower AI preparedness. These factors create a 'double vulnerability' in labor markets, necessitating significant modifications to traditional labor market development approaches to accommodate the impacts of AI and circular economy adoption.
References:
- Circular economy - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_economy
- Skill-Based Labor Market Polarization in the Age of AI: A Comparative Analysis of India and the United States - arxiv.org
- The Micro-Aggregated Profit Share - arxiv.org